In the ever-growing world of data science and machine learning, classification algorithms play a critical role in predictive analytics. One of the most widely used and statistically sound methods is Bayesian classification. Rooted in Bayes’ Theorem, this approach provides a structured way of reasoning under uncertainty, making it a popular choice for spam detection, medical diagnosis, sentiment analysis, and more.
If you’re exploring intelligent decision-making systems, now’s the time to understand how Bayesian classification can enhance your machine learning projects with both simplicity and power.
What is Bayesian Classification?
A Probabilistic Approach to Classification
Bayesian classification is a statistical technique based on Bayes’ Theorem that calculates the probability of a data point belonging to a particular class, given its features. Rather than making hard-and-fast rules, this model applies probabilities to guide decision-making.
Bayes’ Theorem Formula:
P(C∣X)=P(X∣C)⋅P(C)/P(X)
Where:
- P(C|X) is the posterior probability of class C given the input X
- P(X|C) is the likelihood of input X given class C
- P(C) is the prior probability of class C
- P(X) is the evidence or total probability of input X
This formula lies at the heart of Bayesian classification, enabling the model to “learn” from data and make predictions.
Types of Bayesian Classifiers
1. Naive Bayes Classifier
This is the most common type of Bayesian classifier. It makes a strong assumption that all features are conditionally independent given the class label.
- Pros:
- Fast and simple
- Works well with large datasets
- Performs well in text classification and spam detection
- Fast and simple
- Cons:
- The independence assumption may not always hold true
- Less accurate for complex feature interactions
- The independence assumption may not always hold true
2. Bayesian Belief Networks (BBNs)
Also known as Bayesian networks, BBNs are graphical models that show the dependencies among variables.
- Pros:
- Captures complex relationships between features
- Supports inference and reasoning in uncertain environments
- Captures complex relationships between features
- Cons:
- More computationally expensive
- Requires detailed knowledge of probabilistic relationships
- More computationally expensive
Types and Variants of Bayesian Classifiers
While Naive Bayes is the most well-known, several variants of Bayesian classifiers exist to handle different data distributions and relationships.
1. Gaussian Naive Bayes
- Used when features are continuous and follow a normal distribution.
- Commonly applied in medical diagnosis and sensor data classification.
2. Multinomial Naive Bayes
- Suitable for discrete count data — like word frequencies in text documents.
- Widely used in spam detection and document classification.
3. Bernoulli Naive Bayes
- Designed for binary/boolean features (presence or absence).
- Works well for text classification with binary word occurrence indicators.
4. Complement Naive Bayes
- A modification of Multinomial Naive Bayes that improves performance on imbalanced datasets.
- Often used for sentiment analysis and topic categorization.
5. Bayesian Belief Networks (BBNs)
- Represent relationships between variables using directed acyclic graphs (DAGs).
- Each node corresponds to a variable, and edges represent probabilistic dependencies.
- Ideal for reasoning under uncertainty — such as fault diagnosis and medical inference.
6. Semi-Naive Bayesian Classifiers
- Relax some independence assumptions to capture limited feature dependencies without full complexity.
- Example: Tree-Augmented Naive Bayes (TAN).
7. Hierarchical Bayesian Models
- Incorporate multiple levels of parameters for modeling grouped or multi-layer data.
- Commonly applied in biostatistics and econometrics.
Applications of Bayesian Classification in Computer Science
Bayesian classifiers have become indispensable tools in numerous computer science domains because of their interpretability, speed, and robustness.
1.Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Spam Filtering: Classifies emails based on word frequency patterns.
- Sentiment Analysis: Determines the emotional tone of text (positive, negative, neutral).
- Topic Modeling: Automatically groups documents based on thematic content.
2. Information Retrieval and Search Engines
- Ranks and categorizes documents based on relevance scores using probabilistic models.
- Improves personalized recommendations and query understanding.
3. Image and Pattern Recognition
- Bayesian classifiers are used for object detection, face recognition, and handwriting analysis.
- Especially effective when datasets are small or partially labeled.
4. Medical Diagnosis Systems
- Used to predict diseases by combining symptoms, patient history, and test results probabilistically.
- Example: Estimating the probability of diabetes or cancer given observed indicators.
5. Fraud Detection
- Identifies suspicious transactions or activities based on probabilistic patterns in financial data.
- Continuously learns and updates probabilities as new data is observed.
6. Recommender Systems
- Uses prior user behavior to predict what items a user might prefer next.
- Example: Suggesting books, products, or movies on e-commerce platforms.
7. Computer Vision
- Applied in object classification, gesture recognition, and scene understanding using probabilistic models.
8. Speech and Audio Processing
Helps in speech recognition, speaker identification, and emotion detection by modeling the probability of sound patterns.
9. Robotics and Autonomous Systems
- Bayesian reasoning supports navigation, object detection, and sensor fusion in uncertain environments.
- Example: A robot estimating its position using noisy sensor data.
10. Cybersecurity
- Used in intrusion detection systems (IDS) and malware classification by learning from past threat patterns.
Bayes Classification Workflow
The workflow of Bayesian classification follows a structured, step-by-step approach that combines statistical reasoning with learning from data.
Step 1: Data Collection
Gather relevant training data containing features (inputs) and class labels (outputs).
Example: Emails labeled as spam or not spam.
Step 2: Data Preprocessing
Clean and prepare the dataset:
- Handle missing values
- Tokenize text data (if applicable)
- Normalize or discretize features
Step 3: Calculate Prior Probabilities
Compute the initial probability of each class:
P(C)=Number of samples in class C / Total number of samples
Example: 30% spam emails, 70% non-spam.
Step 4: Compute Likelihood
Determine how likely each feature is given a class:
P(X∣C)
Example: The probability that the word “offer” appears in spam messages.
Step 5: Apply Bayes’ Theorem
Combine prior and likelihood to get the posterior probability:
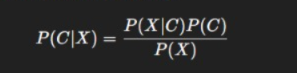
Step 6: Class Prediction
Assign the data point to the class with the highest posterior probability.
Example: If P(spam∣X)>P(not spam∣X), classify as spam.
Step 7: Model Evaluation
Use metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and confusion matrix to measure performance.
Step 8: Deployment
Deploy the trained model into production systems — such as email servers, web apps, or diagnostic platforms.
Key Features of Bayes Classifier
The Bayes classifier is one of the most intuitive and powerful statistical classifiers in machine learning. Its unique features make it both versatile and computationally efficient.
1. Probabilistic Foundation
- The Bayes classifier operates entirely on probabilities rather than deterministic rules.
- It quantifies the likelihood of a class label based on evidence from data.
2. Based on Bayes’ Theorem
- Uses conditional probability to update beliefs based on new information.
- The model continually adjusts as more data becomes available.
3. Simple yet Powerful
- Despite its mathematical simplicity, it performs remarkably well for text classification, spam filtering, and recommendation systems.
4. Robust with Small Datasets
- Works effectively even with limited training samples, making it ideal for early-stage projects or low-data scenarios.
5. Handles Continuous and Categorical Data
- Bayes classifiers can model both numerical and categorical features using appropriate probability distributions.
6. Efficient in High-Dimensional Data
- Performs well in tasks like text classification, where the number of features (words) is extremely high.
7. Handles Missing Data Gracefully
- Missing attributes do not stop the model from making predictions — probabilities are computed from available data.
8. Transparent and Interpretable
- The model’s predictions are explainable through the underlying probability estimates — a key advantage for regulated domains like healthcare and finance.
How Bayesian Classification Works

Step 1: Calculate Prior Probabilities
Estimate the probability of each class from the training data (e.g., how many emails are spam vs. not spam).
Step 2: Calculate Likelihood
Determine how likely each feature is given a class. For example, how often does the word “offer” appear in spam emails?
Step 3: Apply Bayes’ Theorem
Combine prior and likelihood to calculate the posterior probability for each class.
Step 4: Choose the Class with the Highest Posterior
Assign the data point to the class with the highest calculated probability.
Real-World Applications of Bayesian Classification

a. Email Spam Filtering
One of the earliest and most successful uses of Bayesian classification. The algorithm learns common spam words and patterns to flag unwanted emails.
b. Medical Diagnosis
Used to predict diseases based on patient symptoms and history. It calculates the probability of a disease given certain indicators.
c. Sentiment Analysis
Identifies whether a piece of text (like a product review) is positive, negative, or neutral based on keyword frequencies.
d. Document Classification
Helps categorize documents into topics (e.g., finance, sports, technology) based on their content.
Advantages of Bayesian Classification
- Simplicity and Speed:
Particularly, the Naive Bayes version is fast and easy to implement. - Effectiveness with Small Data:
Performs well even with relatively small training datasets. - Handles Missing Data:
The probabilistic nature allows it to make predictions even with incomplete inputs. - Scalability:
Works well for large datasets and high-dimensional feature spaces.
Challenges and Limitations
- Feature Independence Assumption:
In Naive Bayes, this assumption often doesn’t reflect real-world data, which may reduce accuracy. - Sensitivity to Data Quality:
Poor or biased training data can significantly affect performance. - Limited Flexibility:
Compared to models like decision trees or neural networks, Bayesian classifiers may not capture complex patterns as effectively.
Conclusion
Bayesian classification remains a cornerstone of probabilistic modeling, offering speed, interpretability, and solid performance across various applications. Whether you’re building a spam filter, diagnosing diseases, or classifying documents, this technique provides a practical solution grounded in statistical reasoning.
Interested in applying Bayesian classification to your next project? Dive deeper into the world of probability-based machine learning today and build smarter, data-driven systems with confidence.
FAQ’s
What is Bayesian classification?
Bayesian classification is a probabilistic machine learning technique that uses Bayes’ Theorem to predict class membership based on prior knowledge and observed data, making it effective for predictive modeling and decision-making.
What is the Bayesian decision making model?
The Bayesian decision-making model is a statistical approach that uses probabilities and prior knowledge to make optimal decisions under uncertainty by continuously updating beliefs as new data becomes available.
What is the Bayesian predictive model?
The Bayesian predictive model uses Bayes’ Theorem to predict future outcomes by combining prior knowledge with observed data, allowing for more accurate and uncertainty-aware predictions.
What are the advantages of Bayesian classification?
The main advantages of Bayesian classification are:
Simple and fast – Easy to implement and computationally efficient.
Handles missing data well – Can make predictions even with incomplete data.
Probabilistic output – Provides confidence levels for predictions.
Performs well with small datasets – Especially effective when training data is limited.
Robust and scalable – Works well for text classification, spam filtering, and recommendation systems.
What are Bayesian methods used for?
Bayesian methods are used for statistical inference, prediction, and decision-making by updating probabilities as new data becomes available. They’re widely applied in machine learning, data analysis, healthcare, finance, and AI to model uncertainty and improve predictive accuracy.



