Organizations generate massive volumes of data every day. Whether it is e-commerce transactions, social media interactions, medical records, or IoT device data, companies rely on experts to extract meaningful insights.
Data science careers revolve around collecting, cleaning, analyzing, and interpreting data to solve complex problems. Professionals in this field use programming, statistics, and machine learning to develop predictive models and data-driven solutions.
Data science combines multiple domains:
- Statistics
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Domain Knowledge
- Business Strategy
This interdisciplinary nature makes it one of the most dynamic and rewarding career paths today.
Why Data Science Careers Are in High Demand
Several factors contribute to the rise of data science careers:
Explosion of Data
Digital transformation has increased data creation exponentially. Businesses require professionals who can manage and interpret this data.
AI and Machine Learning Growth
The expansion of artificial intelligence has made data science a foundational skill set. Organizations investing in AI need skilled data professionals.
Business Intelligence and Decision Making
Companies depend on predictive analytics for:
- Customer retention
- Revenue forecasting
- Risk analysis
- Fraud detection
According to reports from reputable sources such as IBM and the World Economic Forum, data-related roles are among the fastest-growing jobs globally. You can explore industry insights from IBM’s career portal
Core Skills Required for Data Science Careers
Building a successful career in data science requires both technical and soft skills.
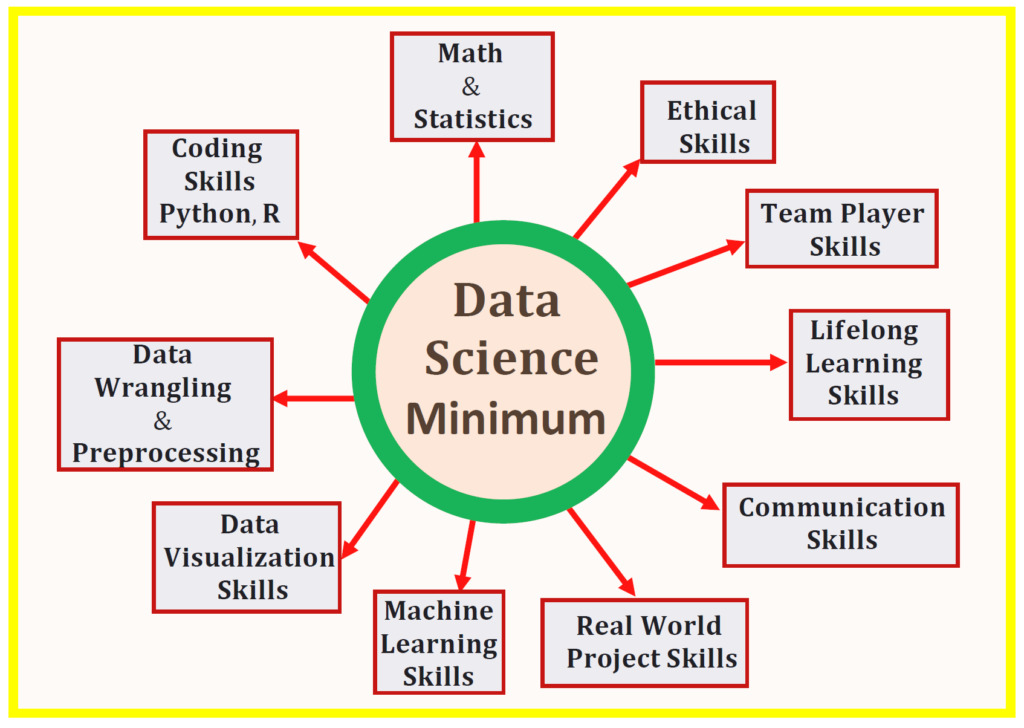
Programming Skills
Common programming languages include:
- Python
- R
- SQL
Python is widely used due to libraries such as:
- Pandas
- NumPy
- Scikit-learn
- TensorFlow
Statistics and Mathematics
Understanding statistical concepts is crucial:
- Probability
- Hypothesis Testing
- Regression Analysis
- Linear Algebra
Data Visualization
Communicating insights effectively is essential. Tools include:
- Tableau
- Power BI
- Matplotlib
- Seaborn
Machine Learning Knowledge
Professionals should understand:
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Classification
- Clustering
- Neural Networks
Soft Skills
- Problem-solving
- Communication
- Business understanding
- Critical thinking
Technical Tools and Technologies
Modern data science careers require familiarity with various tools:
- Jupyter Notebook
- Google Colab
- Apache Spark
- Hadoop
- Git
- Docker
Cloud platforms are increasingly important:
- AWS
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud
Professionals working in machine learning often use frameworks such as:
- TensorFlow
- PyTorch
Educational Pathways and Certifications
There are multiple routes to enter data science careers.
Formal Education
- Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science, Mathematics, Statistics
- Master’s in Data Science
- MBA with Analytics specialization
Online Certifications
Platforms such as Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer recognized certifications.
Relevant certifications include:
- Google Data Analytics Certificate
- IBM Data Science Professional Certificate
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Scientist
For in-depth analytics content, resources from Analytics Vidhya provide practical tutorials and industry insights.
Entry-Level Data Science Careers
If you are starting, consider these roles:
Data Analyst
Responsibilities:
- Cleaning data
- Creating dashboards
- Generating reports
Real-time example: An e-commerce company uses a data analyst to monitor sales trends and customer behavior.
Junior Data Scientist
Tasks include:
- Assisting in model development
- Performing exploratory data analysis
- Supporting senior scientists
Business Intelligence Analyst
Focus on:
- Data visualization
- KPI tracking
- Executive reporting
Mid-Level and Advanced Roles
As experience grows, professionals can move into specialized positions.
Data Scientist
Core responsibilities:
- Build predictive models
- Deploy machine learning systems
- Conduct A/B testing
Example: A fintech company builds a credit scoring model using historical transaction data.
Machine Learning Engineer
Focus on:
- Model deployment
- Production pipelines
- Automation
Data Engineer
Responsible for:
- Building data pipelines
- Managing databases
- Ensuring data quality
Industry-Specific Data Science Careers
Data science careers span multiple industries.
Healthcare
Applications:
- Disease prediction
- Medical imaging analysis
- Personalized treatment plans
Real-time example: Predicting early-stage Parkinson’s disease using voice and movement data.
Finance
Applications:
- Fraud detection
- Algorithmic trading
- Risk assessment
E-commerce
Applications:
- Recommendation systems
- Customer segmentation
- Dynamic pricing
Manufacturing
Applications:
- Predictive maintenance
- Quality control
- Supply chain optimization
Real-Time Examples of Data Science in Action
Recommendation Systems
Streaming platforms use collaborative filtering algorithms to recommend content.
Fraud Detection Systems
Banks use anomaly detection models to flag suspicious transactions.
Predictive Healthcare Analytics
Hospitals use data science models to predict patient readmission risks.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving technology relies on computer vision and deep learning models.
Salaries and Growth Prospects
Data science careers offer competitive compensation.
Approximate salary ranges:
- Entry-Level: Moderate but competitive
- Mid-Level: Strong growth
- Senior-Level: High earning potential
Factors influencing salary:
- Experience
- Location
- Industry
- Skill specialization
How to Transition into Data Science Careers
If you are from a non-technical background:
- Start with statistics fundamentals
- Learn Python
- Practice SQL
- Build projects
If you are from IT:
- Focus on machine learning
- Strengthen statistical understanding
- Create portfolio projects
Portfolio and Project Building Strategy
Your portfolio should include:
- Real-world datasets
- End-to-end projects
- GitHub repository
- Detailed documentation
Sample projects:
- Customer churn prediction
- Stock price forecasting
- Sentiment analysis on Twitter data
Leadership Path in Data Science Careers
As professionals gain experience, data science careers can evolve beyond technical execution into leadership and strategic roles.
Senior-Level Positions
- Senior Data Scientist
- Lead Machine Learning Engineer
- Principal Data Scientist
- Head of Data
- Director of Analytics
- Chief Data Officer (CDO)
Chief Data Officer (CDO)
A Chief Data Officer is responsible for:
- Data governance strategy
- Enterprise-level analytics roadmap
- Regulatory compliance
- AI adoption across departments
- Monetization of data assets
Large enterprises in banking, healthcare, and telecom often appoint a CDO to manage organizational data transformation.
Global Demand for Data Science Careers
Data science careers are not limited to one geography. The demand is global.
High-Demand Regions
- United States
- India
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- Canada
- Australia
In India, companies in Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Pune, and Gurgaon actively recruit for analytics roles.
Remote Work Opportunities
Many organizations now hire remote data professionals. This has increased global competition but also widened opportunities.
Remote-friendly companies often prioritize:
- Strong portfolio
- GitHub activity
- Real-world case studies
- Communication skills
Freelancing and Consulting in Data Science Careers
Not all professionals pursue full-time employment. Many experienced data scientists move into freelancing or consulting.
Freelancing Opportunities
Freelance projects include:
- Predictive modeling
- Data cleaning and dashboard creation
- NLP-based automation
- Business intelligence consulting
Platforms such as Upwork and Toptal list high-paying analytics projects.
Consulting Example
A retail startup might hire a freelance data scientist to:
- Forecast monthly revenue
- Analyze customer churn
- Optimize digital marketing spend
Consulting allows professionals to:
- Work with diverse industries
- Increase earning potential
- Build domain-specific expertise
Specialized Tracks in Data Science Careers
As the field matures, specialization becomes increasingly important.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Used in:
- Chatbots
- Sentiment analysis
- Language translation
- Document classification
Real-time example: Financial firms use NLP to analyze earnings call transcripts.
Computer Vision
Applications:
- Facial recognition
- Medical image analysis
- Autonomous driving systems
- Retail shelf monitoring
Example: Manufacturing companies use computer vision to detect product defects automatically.
Deep Learning
Deep learning powers:
- Speech recognition
- Image generation
- Recommendation engines
- Fraud detection
Professionals skilled in neural networks often command higher salaries.
MLOps (Machine Learning Operations)
MLOps focuses on:
- Model deployment
- Continuous integration
- Monitoring model performance
- Scaling AI systems
This specialization is gaining rapid traction as companies move AI models into production environments.
Industry Case Studies in Data Science Careers
Adding case studies increases authority and real-world relevance.
Case Study: Banking Sector
Problem: Increasing credit default rates
Solution:
- Built predictive models using historical loan data
- Used logistic regression and gradient boosting
- Identified high-risk applicants
Result: Reduced default rate significantly.
Case Study: Healthcare Analytics
Problem: High patient readmission rate
Solution:
- Analyzed patient records
- Built predictive risk model
- Integrated alerts into hospital management system
Result: Improved patient monitoring and reduced readmission costs.
Case Study: E-Commerce
Problem: Low customer retention
Solution:
- Implemented churn prediction model
- Launched personalized offers
- Optimized recommendation engine
Result: Increased repeat purchase rate.
Interview Preparation Strategy for Data Science Careers
Landing a job in data science requires structured preparation.
Technical Interview Focus Areas
- Probability and statistics
- SQL queries
- Data structures
- Machine learning algorithms
- Model evaluation metrics
Practical Rounds
Candidates may be asked to:
- Solve real dataset problems
- Perform exploratory data analysis
- Explain model selection decisions
Behavioral Interview
Recruiters evaluate:
- Communication ability
- Business understanding
- Problem-solving approach
- Team collaboration
Building a Strong LinkedIn Profile for Data Science Careers
Professional branding matters.
Profile Optimization Tips
- Use a headline such as “Aspiring Data Scientist | Machine Learning Enthusiast”
- Add detailed project descriptions
- Share analytics insights
- Publish short technical articles
Recruiters often search LinkedIn using keywords such as:
- Python
- Machine Learning
- Data Visualization
- SQL
Optimizing your profile increases visibility.
Certifications That Add Value
While experience is critical, certifications validate knowledge.
Recommended Certifications
- Google Data Analytics Certificate
- IBM Data Science Professional Certificate
- Microsoft Azure Data Scientist Associate
- AWS Machine Learning Specialty
These certifications enhance credibility and help during career transitions.
Career Transition Roadmap
For Professionals from Non-Technical Background
Step-by-step roadmap:
- Learn Excel and basic statistics
- Move to SQL
- Learn Python fundamentals
- Study machine learning basics
- Build end-to-end projects
For Software Developers
- Strengthen statistics
- Learn ML algorithms deeply
- Work on Kaggle competitions
- Deploy models using cloud services
Kaggle and Competitive Platforms
Kaggle competitions help improve skills.
Benefits:
- Work with real-world datasets
- Learn feature engineering
- Improve model tuning
- Build public profile
Recruiters sometimes value Kaggle rankings.
Ethical Considerations in Data Science Careers
As data-driven systems impact society, ethical concerns grow.
Important Topics
- Data privacy
- Algorithmic bias
- Responsible AI
- Fairness in predictive modeling
Companies increasingly require professionals to understand compliance frameworks and responsible data usage.
Data Science Career vs Related Careers
Understanding the difference helps in career decisions.
Data Scientist vs Data Analyst
Data Scientist:
- Builds predictive models
- Uses machine learning
- Focuses on automation
Data Analyst:
- Generates reports
- Analyzes historical data
- Creates dashboards
Data Engineer vs Data Scientist
Data Engineer:
- Designs data pipelines
- Manages databases
- Ensures scalability
Data Scientist:
- Analyzes data
- Builds models
- Generates insights
Soft Skills That Accelerate Data Science Careers
Technical expertise alone is not enough.
Key Soft Skills
- Storytelling with data
- Presentation skills
- Business communication
- Stakeholder management
A data scientist must translate complex outputs into simple insights for decision-makers.
Long-Term Sustainability in Data Science Careers
Technology evolves rapidly. Continuous learning is mandatory.
How to Stay Updated
- Read research papers
- Follow AI conferences
- Participate in hackathons
- Enroll in advanced courses
- Experiment with new frameworks
Professionals who invest in learning remain competitive.
Entrepreneurship Opportunities
Experienced professionals may start:
- AI consulting firms
- Data analytics startups
- SaaS-based AI products
- Niche industry analytics solutions
For example, startups now provide AI-powered resume screening tools or predictive HR analytics platforms.
Building Domain Expertise
Domain knowledge significantly increases career value.
Popular domains:
- Healthcare analytics
- Fintech analytics
- Retail analytics
- Supply chain analytics
- Marketing analytics
Combining technical skills with domain specialization leads to higher-impact roles.
Future Outlook of Data Science Careers
The future direction includes:
- Generative AI applications
- Real-time predictive systems
- AI-powered automation
- Edge computing analytics
- Explainable AI
Professionals who understand both model building and deployment will dominate the future job market.
Common Challenges in Data Science Careers
- Data quality issues
- Model overfitting
- Business alignment
- Communication gap
Overcoming these challenges requires continuous learning and collaboration.
Future Trends in Data Science
- Generative AI
- Automated Machine Learning
- Responsible AI
- Edge AI
- Real-time analytics
Professionals who adapt to these trends will remain competitive.
Internal Resources
You may also explore related guides on:
- Python Programming
- Google Colab
- Machine Learning Fundamentals
These resources help build a strong foundation for data science careers.
Conclusion
The demand for skilled professionals in analytics and artificial intelligence continues to rise. Organizations across healthcare, finance, retail, and manufacturing rely on data-driven insights for strategic decisions.
Data science careers offer strong growth potential, competitive salaries, and opportunities to work on impactful projects. By developing technical expertise, building real-world projects, and staying updated with industry trends, aspiring professionals can establish a successful and sustainable career in this rapidly evolving field.
This guide has provided an in-depth overview to help you understand the landscape, required skills, tools, roles, and future opportunities in data science careers.



