Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been transforming industries for years. From simple chatbots to advanced recommendation systems, AI has already become an integral part of our daily lives. However, the next frontier in this evolution is Agentic AI—a new paradigm where AI agents are not just reactive tools but autonomous entities capable of making decisions, planning, and executing tasks independently.
Think of Agentic AI as the difference between asking Siri for the weather and having an AI agent plan your day, book your tickets, arrange meetings, and even adjust based on real-time events. This level of autonomy has the potential to reshape business operations, healthcare, education, finance, and beyond.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to artificial intelligence systems designed to act as autonomous agents, capable of reasoning, making decisions, learning continuously, and taking actions in pursuit of defined goals. Unlike traditional AI, which requires explicit instructions for each task, Agentic AI operates with a higher level of initiative and adaptability.
In simple terms, it’s AI that can “think and act” more like a human decision-maker than a programmed machine.
Some key attributes of Agentic AI include:
- Autonomy: Ability to perform tasks without human intervention.
- Adaptability: Learning and evolving based on new data and environments.
- Goal-oriented behavior: Acting toward achieving predefined or dynamically set objectives.
- Reasoning: Considering multiple factors before taking action.
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence
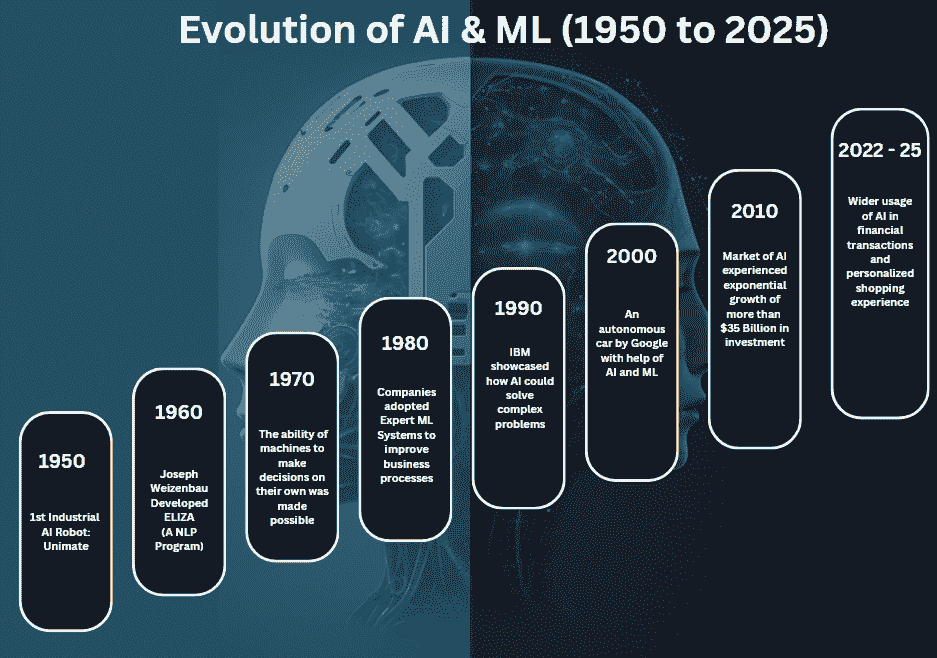
To understand Agentic AI, let’s look at how AI has evolved:
- Rule-based AI – Early systems followed strict “if-this-then-that” logic.
- Machine Learning (ML) – AI began learning patterns from data rather than rules.
- Deep Learning – Neural networks enabled breakthroughs in vision, speech, and NLP.
- Generative AI – Models like ChatGPT and Bard can create human-like text, images, and code.
- Agentic AI – Now, AI systems can act as independent agents, performing multi-step tasks with reasoning and planning abilities.
This progression shows how AI is moving from passive assistance to active problem-solving.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI
Agentic AI is different from conventional AI because of its agency. Here are its defining features:
- Proactive Decision-Making – Acts without waiting for user prompts.
- Multi-Step Task Execution – Can plan and perform tasks that require several steps.
- Context Awareness – Understands and adapts to real-world contexts.
- Collaboration – Works alongside humans or other AI agents to achieve goals.
- Learning Autonomy – Improves performance over time through self-learning.
Example: A customer support AI that not only answers queries but also detects recurring issues, escalates problems, and suggests long-term fixes.
How Agentic AI Works
At its core, Agentic AI relies on three interconnected components:
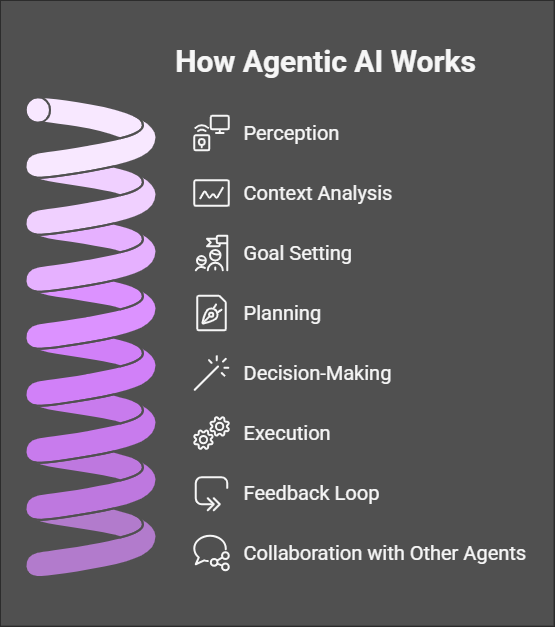
- Perception – Collecting data from the environment (text, images, audio, IoT signals).
- Reasoning – Making sense of the information and deciding on the best action.
- Action – Executing tasks, either digitally (sending emails, updating data) or physically (through robotics).
For instance, an Agentic AI in healthcare could analyze patient symptoms, cross-check medical history, suggest treatments, and schedule doctor appointments—without manual input.
Differences Between Traditional AI and Agentic AI
| Aspect | Traditional AI | Agentic AI |
| Role | Reactive tool | Proactive agent |
| Control | Human-driven | Autonomous |
| Learning | Needs retraining | Self-learning and adapting |
| Decision-making | Narrow focus | Goal-oriented and dynamic |
| Example | Chatbot answering FAQs | AI agent handling end-to-end customer support |
Real-World Examples of Agentic AI
Agentic AI is no longer just a concept—it’s already being implemented in various industries:
- Customer Service – AI agents that handle complex queries, resolve complaints, and upsell products.
- Finance – Autonomous trading systems that analyze markets and execute trades.
- Healthcare – AI agents assisting doctors with diagnoses, patient monitoring, and treatment planning.
- Education – Personalized AI tutors that guide students through adaptive learning paths.
- Supply Chain – AI-driven logistics agents optimizing delivery routes and inventory.
Example: In e-commerce, an Agentic AI can monitor customer behavior, predict preferences, recommend products, and even manage post-purchase support automatically.
Benefits of Agentic AI in Different Industries
- Healthcare: Faster diagnosis, improved patient care, reduced administrative burden.
- Finance: Risk assessment, fraud detection, and automated trading.
- Retail: Personalized shopping experiences and inventory optimization.
- Education: Adaptive learning tools tailored to student needs.
- Manufacturing: Smarter production lines and predictive maintenance.
Challenges and Risks of Agentic AI
While the potential is huge, Agentic AI comes with challenges:
- Ethical Concerns: Ensuring AI doesn’t make biased or harmful decisions.
- Transparency: Understanding how AI makes complex decisions.
- Security Risks: Preventing misuse and ensuring robust cybersecurity.
- Job Displacement: Automation might replace certain human roles.
- Regulation: The need for laws to govern AI’s autonomy.
These challenges highlight the importance of responsible AI development.
Agentic AI in Data Science and Machine Learning
Agentic AI is closely tied to data science and machine learning. It leverages:
- Predictive Models – For anticipating outcomes.
- Reinforcement Learning – For learning through trial and error.
- Natural Language Processing – For interacting with humans effectively.
- Data Analytics – For insights that drive autonomous decision-making.
Example: In marketing, an AI agent can analyze customer behavior, predict churn, create personalized campaigns, and execute them—without needing human intervention at every step.
Future of Agentic AI: Where Are We Heading?
The future of Agentic AI looks incredibly promising:
- Hyper-personalized digital assistants managing daily life.
- Autonomous enterprises where AI runs business operations.
- Collaborative AI ecosystems where multiple AI agents work together.
- Integration with robotics for autonomous physical tasks.
Experts believe that Agentic AI will play a pivotal role in shaping the next generation of human-AI collaboration.
Conclusion
Agentic AI is more than just a buzzword—it represents the future of artificial intelligence. With its ability to act autonomously, adapt continuously, and achieve goals proactively, it holds the potential to revolutionize industries and daily life.
While challenges around ethics, transparency, and regulation remain, the opportunities are immense. From healthcare to finance, retail to education, Agentic AI is paving the way for a smarter, more efficient, and data-driven future.The real question is: Are we ready to embrace AI agents as collaborators in our personal and professional lives?



