In today’s data-first business landscape, making decisions purely on intuition is no longer enough. Organizations need advanced insights that not only explain past events (descriptive analytics) or forecast future outcomes (predictive analytics) but also recommend the best course of action.
That’s where prescriptive analytics comes in.
It goes a step beyond prediction by suggesting what decisions should be made to achieve the desired outcome. Imagine a GPS that doesn’t just predict traffic jams but actually recommends the fastest, most fuel-efficient, and safest route. That’s the role of prescriptive analytics in business.
Why Prescriptive Analytics Matters in the Data-Driven Era
With enterprises generating massive volumes of data every second, the ability to act on data is the competitive edge.
- Businesses leveraging prescriptive analytics can improve decision-making accuracy by up to 30% (Gartner, 2024).
- According to McKinsey, organizations using advanced analytics (including prescriptive models) are twice as likely to outperform their industry peers.
In short: data without action is noise. Prescriptive analytics transforms noise into decisions.
Historical Evolution of Analytics
- Descriptive Analytics → Answers “What happened?”
- Diagnostic Analytics → Answers “Why did it happen?”
- Predictive Analytics → Answers “What will happen?”
- Prescriptive Analytics → Answers “What should we do about it?”
This progression shows how analytics has matured—from hindsight to foresight, and now to decision-making foresight.
How Prescriptive Analytics Works
Prescriptive analytics combines mathematical models, optimization algorithms, AI, and simulation techniques.
Process Flow
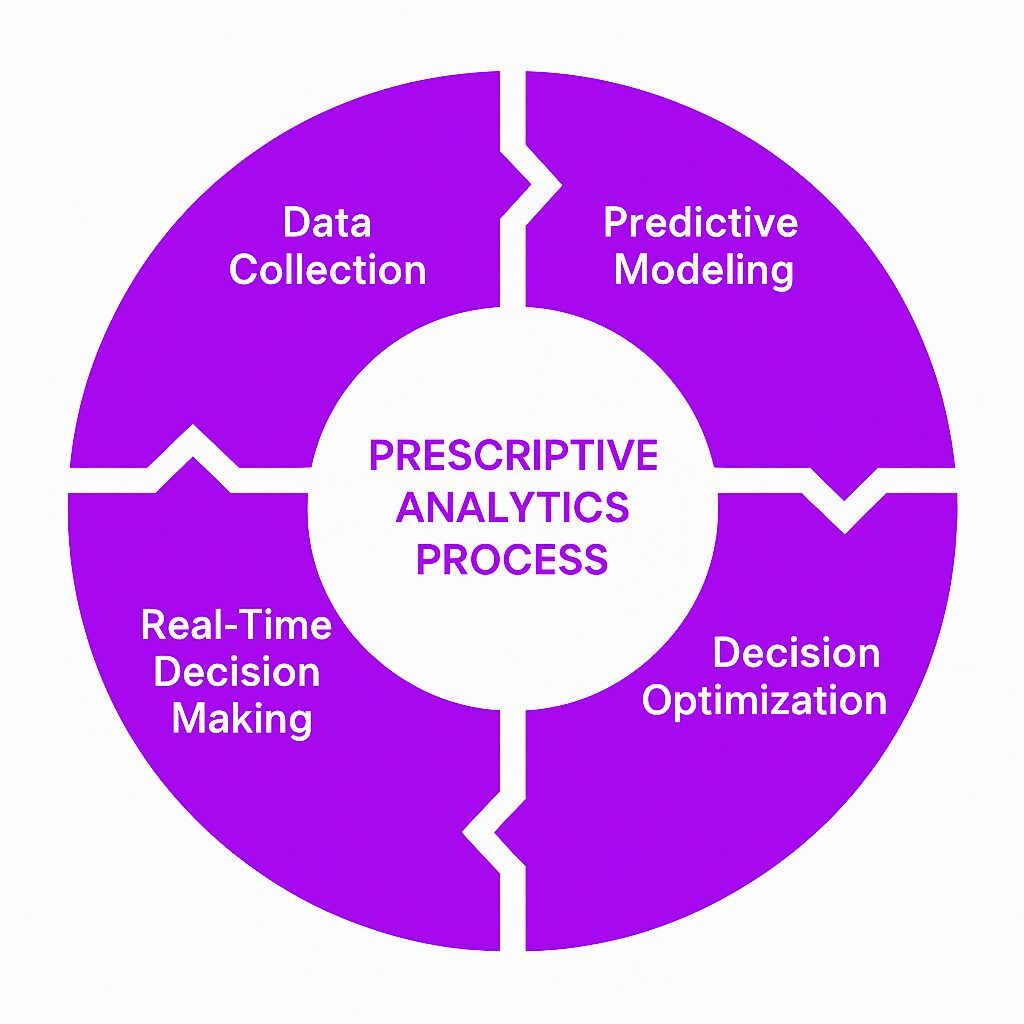
- Data Collection – From multiple sources (databases, IoT, CRM, ERP).
- Data Preparation – Cleaning, preprocessing, and structuring.
- Predictive Modeling – Forecasting possible outcomes.
- Optimization – Evaluating trade-offs among decisions.
- Recommendation – Suggesting the most effective action plan.
Key Components of Prescriptive Analytics
- Machine Learning Models – For pattern detection and forecasting.
- Optimization Algorithms – Linear programming, integer programming.
- Simulation Models – “What-if” analysis.
- Decision Rules – Business logic applied to outcomes.
Real-Time Examples of Prescriptive Analytics in Action
- Airlines use prescriptive analytics for ticket pricing and fuel optimization.
- Retailers like Amazon recommend promotions based on customer behavior.
- Healthcare systems optimize patient scheduling and treatment plans.
- Ride-hailing apps like Uber determine driver allocation and surge pricing.
- Manufacturing firms predict machine failures and recommend preventive maintenance schedules.
Benefits of Prescriptive Analytics for Businesses
- Better decision-making with data-driven recommendations
- Time efficiency through automation of strategic planning
- Cost optimization by reducing waste and maximizing resources
- Improved customer experiences with hyper-personalization
- Competitive edge through proactive decisions
Challenges and Limitations of Prescriptive Analytics
- High data quality requirements
- Complex algorithms that require expert knowledge
- Costly implementation for small businesses
- Ethical challenges in automated decisions
- Dependence on real-time and accurate data
Tools and Technologies for Prescriptive Analytics
- IBM Decision Optimization
- Google OR-Tools
- SAS Advanced Analytics
- Microsoft Azure Machine Learning
- Python libraries: SciPy, Pyomo, Scikit-learn
Prescriptive Analytics vs Predictive Analytics
| Feature | Predictive Analytics | Prescriptive Analytics |
| Focus | Forecast future outcomes | Suggests best action |
| Methods | ML, regression, classification | Optimization, simulation, ML |
| Example | Predict customer churn | Recommend offers to prevent churn |
Prescriptive Analytics in Different Industries
Healthcare
- Optimizing hospital staff schedules
- Personalized treatment recommendations
Retail & eCommerce
- Inventory management
- Personalized product recommendations
Finance & Banking
- Fraud detection with preventive recommendations
- Investment portfolio optimization
Manufacturing & Supply Chain
- Demand forecasting with corrective strategies
- Reducing downtime in production lines
Marketing & Advertising
- Real-time campaign adjustments
- Budget allocation for maximum ROI
Data Requirements and Data Preprocessing
Data preprocessing is vital. It includes:
- Data cleaning (removing duplicates, errors)
- Data integration (from CRM, ERP, IoT)
- Feature selection (choosing relevant variables)
- Data transformation (scaling, normalization)
Without preprocessing, prescriptive analytics cannot deliver accurate recommendations.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Prescriptive analytics and AI go hand in hand:
- Reinforcement Learning – For adaptive decision-making.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – For extracting insights from text.
- Deep Learning – For complex pattern recognition.
Ethical Considerations in Prescriptive Analytics
- Transparency in algorithmic decisions
- Avoiding bias in data and recommendations
- Balancing automation with human oversight
- Data privacy and compliance (GDPR, CCPA)
Prescriptive Analytics in Supply Chain Resilience
- Helps businesses mitigate risks during global disruptions (e.g., pandemics, geopolitical conflicts).
- Provides alternate supplier recommendations in case of shortages.
- Suggests dynamic logistics routing during weather or infrastructure breakdowns.
Prescriptive Analytics in Energy & Utilities
- Forecasts electricity demand and recommends grid balancing actions.
- Identifies optimal energy storage and distribution strategies.
- Supports renewable energy integration by suggesting solar/wind mix optimization.
Prescriptive Analytics in Human Resources
- Optimizes workforce scheduling based on demand peaks.
- Suggests training programs tailored to performance data.
- Assists in employee retention strategies by identifying at-risk staff and interventions.
Role of Cloud Computing in Prescriptive Analytics
- Cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) make advanced analytics scalable and affordable.
- Allows businesses to run optimization models in real time.
- Democratizes access for startups and SMEs.
Real-Time Prescriptive Analytics with Streaming Data
- Traditional analytics is batch-processed, but prescriptive analytics now integrates real-time streaming data from IoT, sensors, and apps.
- Enables instant actions like fraud prevention or dynamic rerouting in logistics.
Prescriptive Analytics in Risk Management
- Identifies potential financial risks in investment portfolios.
- Helps insurers in policy pricing and fraud prevention.
- Suggests mitigation strategies for cybersecurity threats.
Prescriptive Analytics and Customer Experience (CX)
- Hyper-personalized product recommendations.
- Dynamic pricing to match demand without losing loyalty.
- AI chatbots powered with prescriptive rules that suggest next best actions.
Prescriptive Analytics in Cybersecurity
- Recommends incident response strategies during cyberattacks.
- Suggests patch management schedules to reduce vulnerabilities.
- Optimizes firewall and access control rules dynamically.
Advanced Prescriptive Analytics Algorithms
- Linear & Integer Programming – resource allocation.
- Stochastic Optimization – handling uncertainty.
- Evolutionary Algorithms – genetic algorithms for optimal solutions.
- Markov Decision Processes (MDPs) – sequential decision-making.
Hybrid Prescriptive Systems
- Hybrid models combine predictive and prescriptive analytics.
- They predict possible scenarios and then recommend actions across those.
- Increasingly adopted in self-driving cars, where predictions (obstacle detection) and prescriptions (braking, swerving) work together.
Prescriptive Analytics in Public Policy & Governance
- Assists governments in urban planning (traffic control, waste management).
- Recommends optimal allocation of public funds and healthcare resources.
- Helps in disaster response management by suggesting action sequences.
Prescriptive Analytics Success Stories
- Netflix: Uses prescriptive analytics not just to recommend movies but also to decide content production strategies.
- Procter & Gamble: Optimizes supply chains and marketing through prescriptive models.
- FedEx: Leverages prescriptive analytics for package routing, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Skills Required for Prescriptive Analytics Professionals
- Strong foundation in statistics, optimization, and operations research.
- Knowledge of machine learning frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch).
- Familiarity with tools like SAS, IBM Decision Optimization, and Python libraries.
- Business domain knowledge to translate insights into action.
Prescriptive Analytics Implementation Framework
- Define objectives (maximize profit, minimize risk, improve efficiency).
- Collect and clean data.
- Apply predictive models to forecast outcomes.
- Use optimization models to recommend actions.
- Integrate into business workflow with dashboards/automation.
- Monitor and refine continuously.
Visualizing Prescriptive Analytics Outcomes
- Dashboards for scenario comparisons.
- “What-if” simulations with interactive sliders.
- Visualization tools: Tableau, Power BI, Qlik Sense.
Prescriptive Analytics in Marketing Campaigns
- Identifies which customer segment will respond best to specific promotions.
- Suggests budget allocation across multiple channels (Google Ads, social media, TV).
- Helps marketers increase ROI by 20–40% compared to intuition-driven campaigns.
Future Trends in Prescriptive Analytics
- Quantum computing will drastically improve optimization models.
- Automated Prescriptive Analytics (APx) will remove the need for deep technical expertise.
- Integration with Metaverse & AR-based commerce for customer experience optimization.
- Increased focus on explainable prescriptive models for transparency.
Prescriptive Analytics and Real-Time Decision-Making
- Traditional predictive models forecast outcomes, but prescriptive analytics can:
- Recommend immediate actions in time-sensitive scenarios.
- Trigger automated workflows (e.g., auto-adjusting ad spend if ROI drops).
- Apply real-time optimization in financial trading, logistics, and IoT networks.
- Recommend immediate actions in time-sensitive scenarios.
Prescriptive Analytics Career Opportunities
- Prescriptive Analytics Consultant – helps businesses adopt models.
- Data Scientist (Prescriptive Focus) – builds optimization + AI solutions.
- Operations Research Analyst – specializes in mathematical optimization.
- Business Analyst with Prescriptive Analytics Skills – bridges gap between data science and strategy
Ethical Considerations in Prescriptive Analytics
- Risk of bias in recommendations if data is biased.
- Concerns about over-automation — humans must retain decision control.
- Transparency & accountability required in healthcare and finance.
- Companies must ensure privacy compliance (GDPR, HIPAA).
Prescriptive Analytics vs Predictive Analytics: A Deeper Comparison
| Aspect | Predictive Analytics | Prescriptive Analytics |
| Goal | Forecast future trends | Recommend best actions |
| Question Answered | “What is likely to happen?” | “What should we do about it?” |
| Techniques Used | Regression, ML models, time series | Optimization, simulation, AI decision models |
| Output | Probabilities & predictions | Concrete recommendations & strategies |
| Example | Predict demand for next month | Recommend optimal stock levels for warehouses |
Data Sources for Prescriptive Analytics
- Structured Data – databases, CRM, ERP.
- Unstructured Data – emails, social media, customer reviews.
- IoT & Sensor Data – predictive maintenance.
- Historical Data – trends for optimization.
Integration of Prescriptive Analytics with Generative AI
- Generative AI models (like GPT, DALL·E) produce predictions, but prescriptive analytics translates them into actions.
- Together, they can design supply chain plans, create marketing campaigns, and simulate future business outcomes.
Challenges of Prescriptive Analytics
- Data Quality Issues – garbage in, garbage out.
- High Costs – tools, expertise, and infrastructure.
- Change Resistance – employees hesitant to follow algorithmic recommendations.
- Interpretability – business leaders need explainable AI models to trust decisions.
Future of Prescriptive Analytics
The future will see:
- AI-powered prescriptive systems that learn in real-time
- Integration with IoT for smart cities and autonomous vehicles
- Cloud-native solutions democratizing prescriptive analytics for SMEs
- Decision-as-a-Service platforms
By 2030, prescriptive analytics will be embedded into nearly every AI-driven business model.
Conclusion
Prescriptive analytics is no longer optional—it’s the foundation of data-driven decision-making. From healthcare and finance to retail and supply chains, it empowers businesses not just to predict the future but to shape it proactively.
Organizations that embrace prescriptive analytics today will lead tomorrow’s markets.
FAQ’s
What are the 4 types of analytics?
The four types of analytics are Descriptive (what happened), Diagnostic (why it happened), Predictive (what is likely to happen), and Prescriptive (what actions to take)—together guiding smarter, data-driven decision-making.
What is the difference between predictive and prescriptive analytics?
Predictive analytics focuses on forecasting future outcomes using historical data and statistical models, while prescriptive analytics goes a step further by recommending the best actions or strategies to achieve desired results based on those predictions.
What is a real world example of prescriptive analytics?
A real-world example of prescriptive analytics is airline ticket pricing, where airlines use predictive models to forecast demand and then apply prescriptive analytics to recommend the optimal ticket prices, maximizing revenue while keeping flights filled.
Which tool is used in prescriptive analytics?
Common tools used in prescriptive analytics include IBM Decision Optimization, SAS, Gurobi, MATLAB, and Google OR-Tools, which leverage optimization, machine learning, and simulation techniques to recommend the best possible decisions.
Does prescriptive analytics use AI?
Yes, prescriptive analytics often uses AI and machine learning to analyze large datasets, simulate scenarios, and recommend optimal actions. AI enhances prescriptive analytics by enabling smarter decision-making through real-time insights and predictive–prescriptive integration.