Organizations today generate massive volumes of telemetry, logs, clickstreams, and operational data. Traditional relational databases struggle to handle this scale while maintaining low-latency analytics.
Modern analytics requires systems that can ingest data at high velocity, store it efficiently, and query it interactively. This is where specialized analytical engines play a critical role.
Understanding Azure Data Explorer in the Azure Ecosystem
Azure Data Explorer is a fully managed analytics service designed for fast, interactive analysis of large datasets. It is optimized for time-series data, logs, metrics, and event-driven workloads.
Within Microsoft Azure, it serves as a core analytical engine that integrates seamlessly with storage, machine learning, and visualization services.
What Makes Azure Data Explorer Unique
Several characteristics distinguish Azure Data Explorer from other analytics tools.
Key strengths include:
- Extremely fast query performance
- Native support for streaming data
- Powerful compression and indexing
- Scalable architecture without manual tuning
These features make it ideal for real-time analytics scenarios.
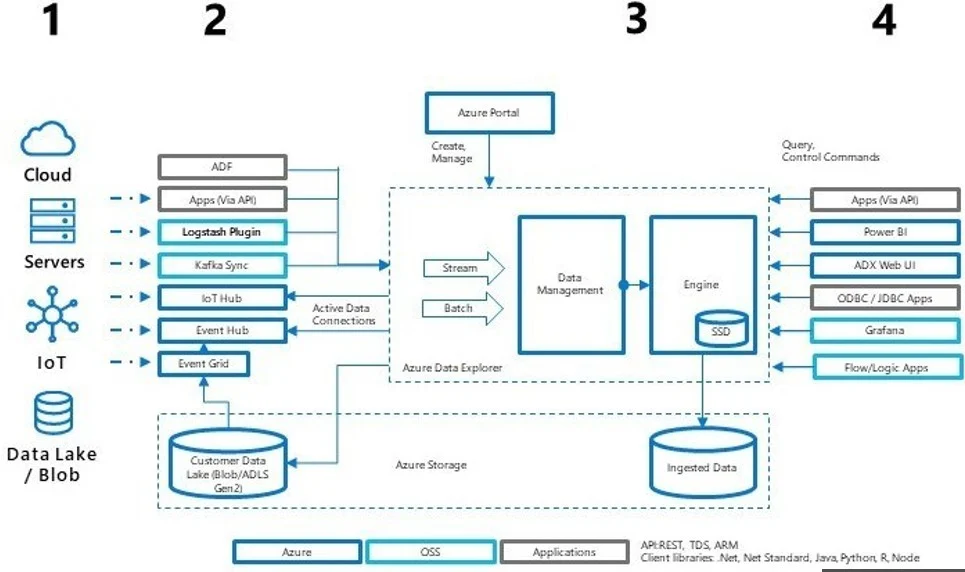
Core Architecture of Azure Data Explorer
The architecture is designed for distributed computing at scale.
Key components include:
- Ingestion layer for streaming and batch data
- Storage layer optimized for columnar data
- Query engine using Kusto Query Language
- Control plane for cluster and resource management
This separation allows independent scaling of compute and storage.
Data Ingestion in Azure Data Explorer
Azure Data Explorer supports multiple ingestion methods.
Common ingestion sources include:
- Event Hubs for streaming telemetry
- Azure Blob Storage for batch ingestion
- Azure Data Factory for scheduled pipelines
- Application logs and monitoring systems
Data can be ingested in near real time with minimal latency.
Querying Data Using Kusto Query Language
Kusto Query Language, commonly called KQL, is the query language used by Azure Data Explorer.
KQL is optimized for:
- Filtering large datasets
- Aggregations over time windows
- Pattern matching and anomaly detection
- Exploratory data analysis
Its syntax is expressive and designed for analytics rather than transactions.
Performance and Scalability Capabilities
Performance is one of the strongest advantages of Azure Data Explorer.
The system achieves this through:
- Columnar storage
- Intelligent indexing
- Distributed query execution
- Automatic caching
Clusters scale horizontally without downtime, making it suitable for enterprise workloads.
Real-Time Analytics Use Cases
Azure Data Explorer is widely used across industries.
Real-world applications include:
- Monitoring application logs
- Detecting security anomalies
- Analyzing IoT telemetry
- Observing user behavior in real time
For example, a SaaS company can analyze millions of events per second to detect system failures instantly.
Azure Data Explorer vs Traditional Databases
Traditional relational databases are designed for transactional workloads.
Azure Data Explorer is designed for analytical workloads.
Key differences include:
- Schema-on-read vs schema-on-write
- Append-only ingestion model
- Optimized for aggregation and scanning
- Minimal locking and contention
This makes it unsuitable for OLTP but perfect for analytics.
Integrating Azure Data Explorer with Azure Storage Explorer
Azure Storage Explorer is a desktop tool used to manage Azure storage resources.
Integration benefits include:
- Browsing Blob Storage containers
- Validating ingested data
- Managing large datasets visually
- Simplifying data lifecycle workflows
This combination improves operational efficiency for data engineers.
Role of Azure Machine Learning in Advanced Analytics
Raw analytics often needs predictive modeling.
Azure Machine Learning enables:
- Training models on historical data
- Deploying models as scalable endpoints
- Managing experiments and pipelines
When combined with Azure Data Explorer, organizations can move from descriptive analytics to predictive and prescriptive analytics.
Azure Machine Learning Studio Explained
Azure Machine Learning Studio is the web-based interface for managing ML workflows.
It provides:
- Experiment tracking
- Dataset management
- Model training and evaluation
- Deployment monitoring
This studio simplifies collaboration between data scientists and engineers.
Azure ML Studio and Model Lifecycle Management
Azure ML Studio supports the complete machine learning lifecycle.
This includes:
- Data preparation
- Feature engineering
- Model training
- Model validation
- Deployment and monitoring
Models trained using data from Azure Data Explorer can be operationalized at scale.
End-to-End Analytics Pipeline Example
A typical enterprise pipeline may look like this:
- Events generated by applications
- Data ingested into Azure Data Explorer
- Queries extract features using KQL
- Data exported to Azure Machine Learning
- Models trained and deployed
- Predictions fed back into analytics dashboards
This closed loop enables continuous improvement.
Security and Governance in Azure Data Explorer
Security is built into the platform.
Capabilities include:
- Role-based access control
- Integration with Azure Active Directory
- Data encryption at rest and in transit
- Audit logging
These features support compliance with enterprise standards.
Monitoring and Cost Optimization
Cost efficiency is critical for large analytics workloads.
Best practices include:
- Monitoring cluster utilization
- Scaling based on query load
- Optimizing ingestion batching
- Archiving cold data
Azure provides native monitoring tools to track usage and performance.
Azure Data Explorer for Time-Series Analytics
Time-series data is one of the most common data types in modern systems. Application logs, IoT sensor readings, monitoring metrics, and user events are all generated continuously over time.
Azure Data Explorer is purpose-built to handle this kind of data efficiently. Its internal storage engine is optimized for time-based queries, allowing analysts to filter, aggregate, and visualize trends over large time windows with minimal latency.
Common time-series operations include:
- Trend analysis over days or months
- Rolling averages and moving windows
- Peak detection and anomaly identification
- Time-based grouping and summarization
These capabilities make Azure Data Explorer a preferred choice for observability and monitoring platforms.
Azure Data Explorer in IoT and Streaming Scenarios

Internet of Things platforms generate massive volumes of telemetry data. Devices send readings continuously, often at high frequency.
Azure Data Explorer integrates seamlessly with Event Hubs and IoT Hub, enabling near real-time ingestion and analysis of streaming data. Engineers can monitor device health, detect anomalies, and trigger alerts based on live conditions.
For example, a manufacturing company can analyze sensor data to detect equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Advanced Query Optimization Techniques in KQL
Writing efficient Kusto Query Language queries is essential for performance and cost control.
Best practices for query optimization include:
- Filtering early to reduce data scanned
- Using summarize operators effectively
- Avoiding unnecessary joins on large tables
- Leveraging materialized views for frequent queries
Well-optimized queries not only improve speed but also reduce compute usage.
Materialized Views in Azure Data Explorer
Materialized views store precomputed query results that update automatically as new data arrives.
They are useful when:
- Queries are complex and frequently executed
- Low-latency results are required
- Large datasets are queried repeatedly
By using materialized views, organizations can significantly reduce query execution time and improve dashboard responsiveness.
Azure Data Explorer and Power BI Integration
Visualization is a critical part of analytics.
Azure Data Explorer integrates natively with Power BI, allowing users to build interactive dashboards on top of KQL queries. This enables business users to explore real-time data without writing complex queries.
Power BI dashboards backed by Azure Data Explorer are commonly used for:
- Operational monitoring
- Business performance tracking
- Incident analysis
- Executive reporting
Using Azure Data Explorer with Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics and Azure Data Explorer serve different but complementary roles.
Azure Synapse is optimized for large-scale data warehousing and batch analytics, while Azure Data Explorer excels at real-time analytics.
Together, they enable:
- Hot data analysis using Azure Data Explorer
- Historical and aggregated analysis using Synapse
- Seamless data movement between systems
This hybrid approach supports both real-time and long-term analytical needs.
Data Retention and Lifecycle Management
Not all data needs to be stored forever.
Azure Data Explorer allows organizations to define retention policies that automatically manage data lifecycle. Hot data can be retained for fast access, while older data can be archived or exported to lower-cost storage.
Effective retention strategies help control costs while maintaining analytical value.
Azure Data Explorer Security Best Practices
Securing analytical data is critical, especially in regulated industries.
Recommended security practices include:
- Implementing role-based access control
- Using Azure Active Directory integration
- Limiting query permissions by user role
- Auditing access and usage patterns
These practices ensure that sensitive data is accessed only by authorized users.
Azure Data Explorer in DevOps and Site Reliability Engineering
DevOps and SRE teams rely heavily on logs and metrics.
Azure Data Explorer is commonly used to:
- Analyze application logs
- Monitor infrastructure performance
- Investigate incidents and outages
- Perform root cause analysis
Its fast query performance enables teams to respond to issues quickly and confidently.
Cost Management Strategies for Azure Data Explorer
While powerful, analytics platforms must be cost-effective.
Cost optimization strategies include:
- Choosing appropriate cluster sizes
- Monitoring ingestion volume
- Using compression-friendly data formats
- Cleaning unnecessary or duplicate data
Azure monitoring tools help track usage and prevent unexpected costs.
Azure Data Explorer vs Azure Log Analytics
Although both services analyze logs, they serve different purposes.
Azure Log Analytics focuses on operational monitoring, while Azure Data Explorer is a general-purpose analytics engine with broader use cases.
Azure Data Explorer provides:
- Greater query flexibility
- Higher performance for large datasets
- Advanced analytical capabilities
Organizations often use both services together.
Azure Data Explorer in Data Science Workflows
Data scientists use Azure Data Explorer during exploratory data analysis.
Its fast response times allow:
- Rapid hypothesis testing
- Feature extraction
- Data validation before modeling
Exported results can then be fed into Azure Machine Learning pipelines for training and experimentation.
Governance and Compliance Considerations
Enterprises operating in regulated environments must ensure compliance.
Azure Data Explorer supports compliance through:
- Encryption standards
- Audit logging
- Data access controls
- Integration with Azure governance tools
This makes it suitable for industries like finance, healthcare, and telecommunications.
Future Trends in Azure Data Explorer Usage
As real-time analytics becomes more critical, Azure Data Explorer continues to evolve.
Emerging trends include:
- Increased adoption in AI-driven monitoring
- Integration with generative AI workflows
- Expansion into predictive analytics pipelines
- Deeper integration with Azure AI services
These trends position it as a long-term strategic platform.
Strategic Takeaway for Data Leaders
Azure Data Explorer is more than a querying tool. It is a foundational analytics platform that enables organizations to move from raw data to actionable insight at scale.
When combined with Azure Machine Learning, Azure ML Studio, and Azure Storage Explorer, it forms a powerful, end-to-end analytics ecosystem capable of supporting modern, data-driven enterprises.
Best Practices for Enterprise Deployments
Successful implementations follow clear guidelines.
Recommended practices include:
- Designing ingestion for high throughput
- Partitioning data by time
- Using materialized views for frequent queries
- Separating workloads across clusters
These strategies improve reliability and performance.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Common challenges include:
- Over-ingesting unnecessary data
- Writing inefficient KQL queries
- Ignoring cost monitoring
- Mixing transactional and analytical workloads
Avoiding these mistakes improves long-term success.
Final Thoughts and Strategic Takeaways
Azure Data Explorer plays a critical role in modern cloud analytics by enabling fast, scalable, and interactive analysis of massive datasets. When combined with Azure Machine Learning, Azure ML Studio, and Azure Storage Explorer, it forms a complete analytics ecosystem.
Organizations that adopt this stack gain real-time visibility, predictive intelligence, and operational efficiency, making it a strategic choice for data-driven enterprises.
FAQ’s
What is the purpose of Azure Data Explorer?
Azure Data Explorer is designed for fast ingestion and analysis of large volumes of time-series, log, and telemetry data, enabling real-time insights through powerful querying and analytics.
What Azure service is a limitless analytics service that brings together big data and data warehousing?
Azure Synapse Analytics is the Azure service that combines big data analytics and data warehousing into a single, limitless analytics platform for end-to-end data insights.
What is the difference between Azure Data Explorer storage optimized and compute optimized?
Storage-optimized clusters focus on cost-efficient data storage with moderate query performance, while compute-optimized clusters provide higher processing power for faster, more complex queries on large datasets.
What is the difference between Azure Data Explorer and Synapse analytics?
Azure Data Explorer is optimized for real-time analysis of logs, telemetry, and time-series data, while Azure Synapse Analytics is designed for large-scale data warehousing and big data analytics across structured and unstructured data.
What are three functions of data Explorer?
Three key functions of Data Explorer are fast data ingestion, real-time query and analysis, and interactive data visualization, enabling quick insights from large datasets.



