Introduction to Edge Computing
Edge computing represents a transformative approach to data processing and network architecture, designed to bring computation and data storage closer to the location where it is needed, to improve response times and save bandwidth. This blog delves into the advanced applications of edge computing and examines its real-world impacts, which are reshaping industries by enabling smarter, more responsive technology systems.
Edge computing is increasingly recognized as a critical infrastructure in the era of the Internet of Things (IoT) and beyond. By processing data near its source, edge computing minimizes latency and bandwidth use, enabling more efficient and agile responses in a myriad of applications from autonomous vehicles to personalized retail experiences.
The Technology Behind Edge Computing
At its core, edge computing involves processing data geographically closer to where it is generated, unlike traditional cloud computing networks that operate in centralized data centers. This shift dramatically reduces latency, enhances the speed of data processing, and supports real-time decision-making across various sectors.
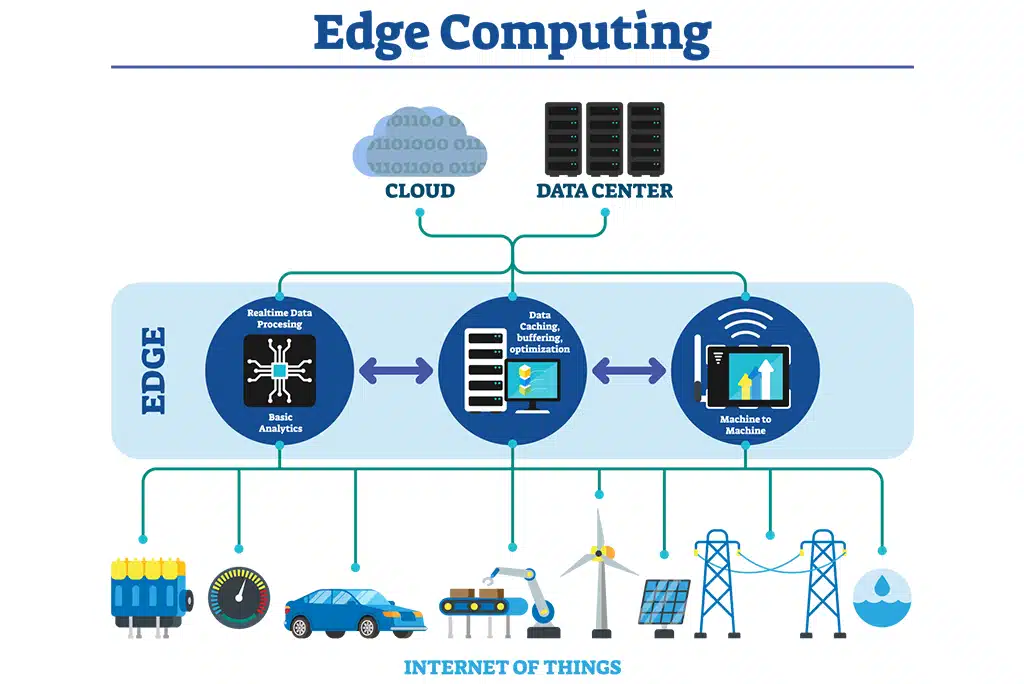
Edge computing’s decentralized nature requires robust networking and seamless communication between distributed devices and central servers. This technological backbone is vital to handle the vast amounts of data generated by devices at the “edge” of the network, ensuring that data latency and server loads are significantly reduced.
Advanced Applications of Edge Computing
The advanced applications of edge computing are diverse and expanding rapidly as industries recognize its potential. By enabling real-time data processing without the need for constant connectivity to a central data center, applications of edge computing support areas that require immediate analytical feedback and where rapid response times are critical.
Smart Cities
In smart cities, applications of edge computing play a crucial role in traffic management and public safety. By processing data locally at traffic signals and surveillance cameras, helps in immediate decision-making to enhance urban living.
In addition to traffic management and public safety, edge computing in smart cities extends to energy management and environmental monitoring. By leveraging real-time data from sensors distributed throughout the city, edge computing enables more efficient resource allocation, reducing energy consumption and improving sustainability. These systems can dynamically adjust lighting, heating, and cooling in public buildings based on current environmental conditions and occupancy.
- Waste Management: Optimizes garbage collection routes and schedules.
- Water Management: Monitors water quality and usage to detect leaks and conserve water.
- Smart Parking: Reduces traffic congestion by providing real-time parking availability data.
Applications of Edge Computing in Healthcare
Edge computing revolutionizes healthcare by facilitating real-time remote monitoring and diagnostics, greatly enhancing patient care. Localized data processing ensures that patient data is analyzed promptly, leading to quicker response times in critical situations.
Beyond enhancing patient care through monitoring and diagnostics, edge computing supports telemedicine and emergency medical services. By enabling faster data processing at the point of care, it helps healthcare providers offer timely treatments and make critical decisions faster. Edge computing can manage the large volumes of data generated by medical imaging devices, allowing for quicker image processing and analysis directly at care facilities.
- Telemedicine: Facilitates real-time patient-practitioner interactions from remote locations.
- Emergency Response: Speeds up response times with real-time data access during medical emergencies.
- Medical Research: Accelerates data analysis for research purposes, improving the speed of clinical trials.
Edge Computing in Manufacturing
The applications of edge computing in manufacturing enhance operational efficiency through real-time monitoring of production lines. It allows for instant quality control and predictive maintenance, minimizing downtime and reducing costs.
Applications of Edge computing also support the integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) on the manufacturing floor, enhancing the training and precision of complex assembly tasks. By processing data on the edge, manufacturers can use AR overlays to guide assembly line workers in real-time, reducing errors and improving product quality.
- Asset Tracking: Real-time location systems track assets throughout the manufacturing process for better logistics.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Provides real-time insights into supply chain operations, enabling proactive management.
- Worker Safety: Monitors environmental conditions to ensure worker safety and compliance with regulations.
Applications of Edge Computing in Retail
The applications of Edge computing transform the retail experience by enabling personalized customer experiences through real-time data analysis. It supports inventory management and optimizes the supply chain by processing information instantaneously at each retail location.
Edge computing further revolutionizes retail by enabling dynamic pricing and targeted advertising. By analyzing customer data and inventory levels in real time, retailers can adjust prices on the fly to optimize sales and reduce inventory overhead. Additionally, edge computing can enhance in-store navigation and personalized marketing strategies, offering promotions directly to consumers’ smartphones as they browse relevant store sections.
- Dynamic Pricing: Adjusts prices in real-time based on demand and inventory.
- Customer Engagement: Enhances customer interaction with personalized digital experiences.
- Loss Prevention: Monitors and responds to potential theft incidents more quickly with real-time surveillance analytics.
How Does Edge Computing Function?
Edge computing functions by processing data at or near the source where it is generated, rather than transmitting all data to a centralized cloud or data center. This decentralized model enables faster decision-making, reduced latency, and optimized bandwidth usage.
Step-by-Step Edge Computing Workflow
- Data Generation at the Edge
Data is produced by edge devices such as sensors, cameras, wearables, industrial machines, or IoT devices. - Local Data Processing
Instead of sending raw data to the cloud, edge devices or nearby edge servers analyze and process data locally using embedded compute power. - Real-Time Decision Making
Critical insights or actions are generated instantly—for example, triggering alerts, adjusting machinery, or responding to user behavior. - Selective Cloud Communication
Only relevant, summarized, or non-sensitive data is transmitted to the cloud for long-term storage, advanced analytics, or historical analysis. - Continuous Feedback Loop
Edge systems continuously learn and adapt, often integrating AI and machine learning models for predictive and autonomous decision-making.
This architecture enables high-speed, resilient, and intelligent systems, especially in environments where latency and connectivity are critical.
Key Advantages of Edge Computing
Edge computing delivers significant benefits that extend beyond performance improvements.
1. Ultra-Low Latency
Processing data locally reduces delays, making edge computing ideal for real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
2. Reduced Bandwidth Usage
By filtering and processing data at the edge, only essential information is sent to the cloud, lowering network congestion and transmission costs.
3. Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
Sensitive data can be processed locally, reducing exposure to cyber threats and supporting compliance with data privacy regulations.
4. Improved Reliability
Edge systems continue functioning even during network disruptions, ensuring uninterrupted operations in mission-critical environments.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Edge architectures can scale easily by adding new devices without overloading centralized infrastructure.
6. Faster Insights and Actions
Immediate analytics enable proactive responses rather than reactive decisions, improving operational efficiency.
Real-World Applications of Edge Computing
Edge computing is actively transforming industries by enabling intelligent, responsive systems.
Smart Cities
- Real-time traffic management
- Smart lighting and energy optimization
- Public safety monitoring
Healthcare
- Remote patient monitoring
- Real-time medical imaging analysis
- Emergency response systems
Manufacturing
- Predictive maintenance
- Quality inspection using computer vision
- Industrial robotics and automation
Retail
- Personalized in-store experiences
- Inventory tracking and demand forecasting
- Fraud detection and loss prevention
Transportation and Logistics
- Fleet monitoring
- Route optimization
- Autonomous vehicle navigation
Edge Computing Examples Across Industries
Automotive Industry
- Autonomous driving systems process sensor data in milliseconds
- Driver behavior and fatigue detection
- Smart navigation and collision avoidance
Energy and Utilities
- Smart grid management
- Real-time fault detection
- Renewable energy optimization
Telecommunications
- 5G network optimization
- Low-latency streaming services
- Edge-enabled content delivery networks (CDNs)
Agriculture
- Precision farming using real-time sensor data
- Automated irrigation systems
- Crop health monitoring
Media and Entertainment
- Real-time video processing
- Augmented and virtual reality experiences
- Personalized content delivery
Real-World Impact of Edge Computing
The deployment of edge computing technologies has led to significant improvements in service delivery and operational efficiency. Its impact is evident in faster processing times, reduced latency, and enhanced data security, proving essential in situations where immediate data processing is crucial.
The real-world impacts of edge computing are profound, reshaping how data-driven decisions are made across industries.
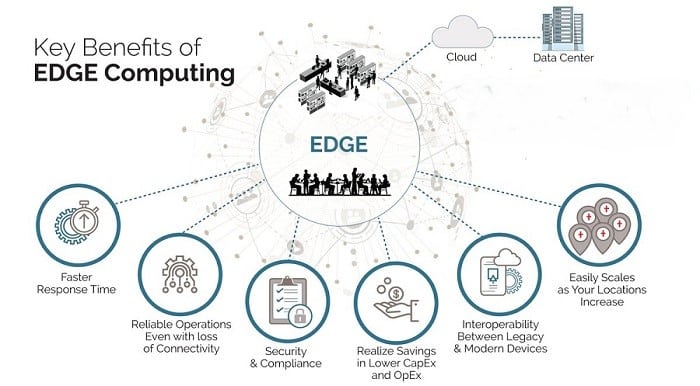
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Faster processing speeds improve operational tasks.
- Improved Safety Measures: Immediate data analysis can predict and mitigate potential hazards in industries like manufacturing and transportation.
- Reduced Costs: By processing data locally, companies save on data transmission costs and reduce their reliance on cloud services.
- Data Privacy Enhancements: Local data processing helps comply with privacy regulations by minimizing the amount of sensitive data transferred.
Challenges and Solutions in Edge Computing
While edge computing offers substantial benefits, it also poses unique challenges such as data security risks, infrastructure costs, and management complexity. Solutions include the implementation of robust security protocols, investing in scalable infrastructure, and using advanced management software to handle widespread edge devices.
Edge computing, while transformative, introduces specific challenges that need addressing to maximize its potential.
- Security Concerns: Each edge device can be a potential entry point for security breaches.
- Complexity in Management: Managing numerous edge devices can be cumbersome without the right tools.
- Integration Issues: Seamlessly integrating edge devices with existing IT environments remains a challenge.
Future Trends in Edge Computing
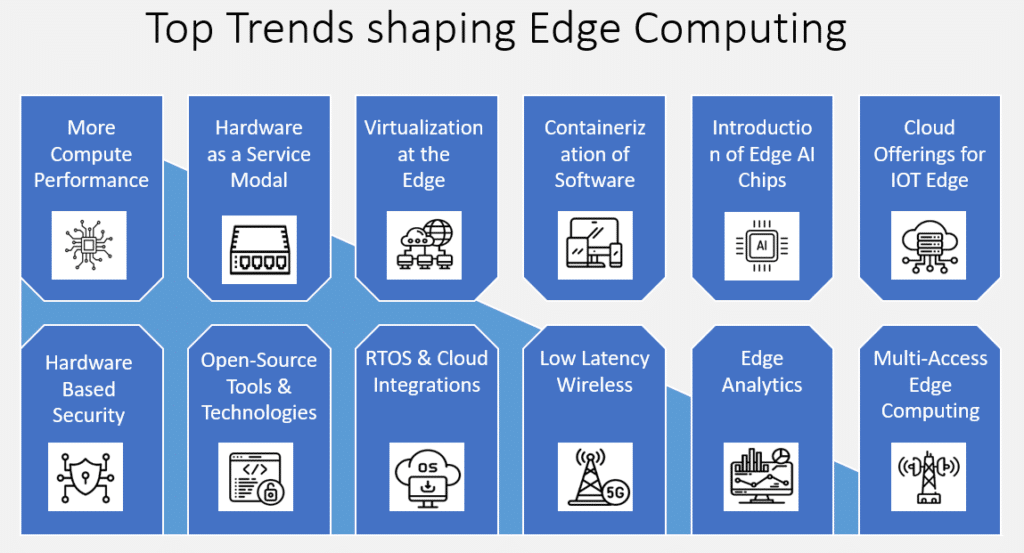
The future of edge computing looks promising, with ongoing advancements expected to further integrate AI and machine learning capabilities. These trends are likely to enhance the automation and cognitive abilities of edge computing systems, making them more adaptive and intelligent.
- AI Integration: Enhancing processing capabilities at the edge.
- Increased Device Autonomy: Devices will perform more complex processing independently.
- Wider Adoption Across Industries: As benefits become clearer, more sectors will adopt edge computing.
As edge computing matures, it is set to revolutionize sectors by integrating more deeply with AI and machine learning, leading to smarter edge devices capable of autonomous decision-making. This integration predicts a future where edge computing not only supports but actively drives business intelligence and operations.
Conclusion
Applications of edge computing across multiple industries are poised to establish it as a cornerstone technology, supporting a wide range of functions and enhancements. Its ability to process data close to the source dramatically improves efficiency, responsiveness, and overall system performance. As technology evolves, edge computing is expected to play an even larger role in our digital future.
Edge computing stands at a transformative junction in the landscape of network technology. As we continue to generate more data and demand quicker, more reliable insights, edge computing will be integral in shaping the future of digital business operations. Its ability to process and analyze data locally is not just an operational upgrade but a strategic advantage that will define the competitive edge for businesses in the digital age.
FAQ’s
How does edge computing impact real-time applications?
Edge computing reduces latency by processing data closer to the source, enabling faster responses and more efficient performance for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and IoT devices.
What are the applications of edge computing?
Edge computing is applied in IoT devices, autonomous vehicles, smart cities, industrial automation, healthcare monitoring, video streaming, and augmented/virtual reality, where low-latency, real-time data processing is critical.
What are the real life examples of edge AI?
Real-life examples of Edge AI include autonomous vehicles detecting obstacles, smart cameras for security, wearable health monitors, industrial robots performing quality checks, and smart home devices like voice assistants that process data locally for faster responses.
What is edge full form?
The full form of EDGE is Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution, a technology that improves data transmission speeds in mobile networks.
What is the main benefit of edge computing?
The main benefit of edge computing is reduced latency and faster processing by analyzing data closer to the source, which enhances real-time decision-making and overall system efficiency.



