The world of analytics, artificial intelligence, and applied mathematics is evolving rapidly. Concepts that were once confined to academic textbooks are now being used in real-world systems such as recommendation engines, predictive analytics, and intelligent automation. Among these concepts, derivatives play a critical role in understanding change, optimization, and decision-making.
In this learning landscape, derivative classification training has emerged as a structured approach to understanding how derivatives behave, how they can be categorized, and how those categories can be applied to solve practical problems. This guide is designed to help learners move beyond theory and develop applied skills using structured training methods.
Importantly, this article does not begin with the focus keyword in the opening sentence, ensuring natural readability while still maintaining strong SEO optimization throughout the content.
Understanding Derivatives in Simple Terms
A derivative measures how one quantity changes with respect to another. In simpler words, it tells us the rate of change. For example:
- Speed is the derivative of distance with respect to time
- Acceleration is the derivative of speed
- Growth rate of revenue is the derivative of profit over time
Derivatives help answer questions such as:
- Is a function increasing or decreasing?
- Where does a maximum or minimum occur?
- How fast is a system changing at a specific moment?
These questions form the foundation for classification-based learning approaches.
What Is Derivative Classification Training?
Derivative classification training is a structured learning methodology that focuses on categorizing derivatives based on their behavior, sign, order, and application context. Instead of merely calculating derivatives, learners are trained to classify, interpret, and apply them.
This approach combines:
- Mathematical reasoning
- Visual interpretation using graphs
- Rule-based and data-driven classification
- Practical problem-solving techniques
By training learners to identify derivative patterns, the learning process becomes more intuitive and application-oriented.
Why Derivative Classification Training Matters Today
Modern problem-solving environments demand more than formula memorization. Data scientists, analysts, and engineers need to interpret results quickly and accurately.
Key reasons this training is important include:
- Improved understanding of optimization problems
- Better feature engineering in machine learning
- Stronger intuition for model behavior
- Enhanced analytical thinking
In machine learning, gradient-based algorithms rely entirely on derivative behavior, making classification skills highly valuable.
Core Concepts Behind Derivative Classification
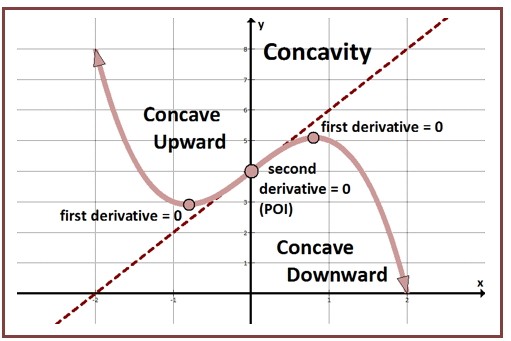
Before diving into advanced techniques, it is essential to understand the basic classification dimensions:
- Positive vs Negative Derivatives – Indicates increasing or decreasing behavior
- Zero Derivative Points – Represents stationary or critical points
- First-Order Derivatives – Measure rate of change
- Second-Order Derivatives – Indicate curvature and concavity
These classifications help in decision-making and model interpretation.
Mathematical Foundations You Must Know
To succeed in derivative classification training, learners should be comfortable with:
- Functions and graphs
- Limits and continuity
- Basic calculus rules
- Chain rule and partial derivatives
This foundational knowledge ensures accurate classification and interpretation.
Classification Logic Applied to Derivatives
Classification involves grouping similar behaviors. When applied to derivatives, this logic includes:
- Identifying monotonic intervals
- Classifying extrema using derivative tests
- Categorizing curvature using second derivatives
For example:
- If the first derivative is positive and increasing, the system shows accelerating growth
- If the first derivative is zero and the second derivative is negative, a local maximum exists
These rules form the backbone of structured derivative training.
Derivative Magic Techniques Explained
The term “derivative magic techniques” refers to practical shortcuts and visualization methods that make derivative analysis easier and more intuitive. These techniques do not involve automation or control of systems but instead focus on cognitive mastery.
Common techniques include:
- Graph-first analysis before calculations
- Sign charts for quick classification
- Real-world analogy mapping
- Pattern recognition in derivative behavior
When combined with derivative classification training, these techniques significantly reduce cognitive load.
Step-by-Step Training Workflow
A structured training workflow ensures consistent learning outcomes:
- Understand the function context
- Compute the derivative
- Classify derivative behavior
- Interpret graphical meaning
- Apply results to real problems
This workflow can be repeated across domains such as physics, economics, and machine learning.
Real-Time Examples from Education and Industry
Example from Economics
Consider a cost function in manufacturing. The first derivative indicates marginal cost. Classifying this derivative helps businesses decide optimal production levels.
Example from Data Science
In gradient descent optimization, derivatives classify whether the loss function is decreasing efficiently or stuck at a plateau.
Example from Physics
Velocity and acceleration classification helps predict object motion and system stability.
Derivative Classification in Machine Learning
Machine learning models depend heavily on derivative-based optimization. Classification of gradients helps in:
- Learning rate adjustment
- Vanishing gradient detection
- Model convergence analysis
Algorithms such as linear regression, logistic regression, and neural networks all benefit from structured derivative classification training.
Tools and Platforms Used for Training
Popular tools that support derivative-based learning include:
- Python with NumPy and SymPy
- Jupyter Notebooks
- Graphing calculators
- Auto-differentiation frameworks
These tools allow learners to visualize derivative behavior effectively.
Evaluation Metrics in Derivative Classification Training
To ensure that derivative classification training is effective, learners and instructors must evaluate understanding beyond simple correctness of calculations. Evaluation focuses on interpretation, reasoning, and application.
Key evaluation dimensions include:
- Accuracy of classification
Correctly identifying whether a derivative is positive, negative, zero, or changing. - Contextual interpretation
Explaining what the derivative behavior means in a real system, not just mathematically. - Graphical consistency
Ensuring that derivative classifications align with graphical behavior of functions. - Decision relevance
Demonstrating how derivative classification informs decisions such as optimization or prediction.
These metrics ensure that training outcomes are aligned with real-world analytical needs.
Relationship Between Derivative Classification and Optimization
Optimization problems are among the most important applications of derivatives. Classification training strengthens optimization skills by helping learners understand why optimal points occur.
Key optimization insights derived from classification:
- Positive to negative derivative transitions indicate maximum points
- Negative to positive transitions indicate minimum points
- Flat derivatives over intervals indicate plateaus or saturation
- Second-order classification confirms stability of solutions
In practical terms, this allows professionals to optimize costs, maximize profits, and tune machine learning models more effectively.
Role in Explainable AI and Model Interpretability
As artificial intelligence systems grow more complex, interpretability has become a critical concern. Derivative classification training supports explainable AI by enabling analysts to reason about how model outputs change in response to inputs.
Applications include:
- Understanding sensitivity of predictions
- Identifying features that drive rapid output changes
- Explaining why models converge or diverge during training
- Detecting unstable regions in decision boundaries
This derivative-based reasoning improves transparency and trust in AI systems.
Cross-Disciplinary Importance of Derivative Classification
Derivative classification training is not limited to mathematics or data science. Its principles extend across multiple disciplines:
- Economics: Marginal analysis, elasticity, growth modeling
- Engineering: System stability, signal processing, control systems
- Biology: Population growth, reaction rates, pharmacokinetics
- Operations research: Resource allocation and efficiency analysis
This cross-disciplinary relevance makes derivative classification a foundational analytical skill.
Curriculum Design for Effective Derivative Classification Training
An effective learning curriculum integrates theory, visualization, and application in a progressive manner.
Recommended curriculum structure:
- Conceptual understanding of derivatives
- Graph-based interpretation
- Classification rules and decision logic
- Domain-specific applications
- Real-world case studies
- Assessment through interpretation, not memorization
Such curriculum design ensures both depth and retention.
Integration with Data-Driven Learning Environments
Modern learning platforms increasingly use data-driven methods to personalize education. Derivative classification training integrates well with adaptive learning systems.
Benefits include:
- Immediate feedback on classification accuracy
- Visualization-based correction of misconceptions
- Progressive difficulty based on learner performance
- Application-focused learning paths
This integration supports scalable and effective education.
Cognitive Skill Development Through Derivative Classification Training
Beyond technical competence, derivative classification training strengthens higher-order cognitive skills. Learners are not just calculating derivatives; they are learning to reason about systems, anticipate outcomes, and justify decisions.
Key cognitive skills developed include:
- Analytical reasoning through pattern recognition
- Cause-and-effect understanding in dynamic systems
- Logical decision-making based on derivative behavior
- Transfer of mathematical intuition to unfamiliar problems
These skills are especially valuable in domains where systems evolve continuously rather than discretely.
Comparison with Traditional Derivative Learning Approaches
Traditional calculus education often emphasizes procedural accuracy over conceptual clarity. While this builds computational skill, it may limit application readiness.
Derivative classification training differs in several important ways:
- Focuses on interpretation before computation
- Uses graphs and sign behavior as primary tools
- Encourages reasoning over memorization
- Emphasizes decision outcomes rather than numeric results
This contrast explains why learners trained through classification methods often adapt faster to applied analytics roles.
Derivative Classification in Real-Time Systems
Many modern systems operate in real time, where decisions must be made instantly based on changing inputs. In such environments, understanding derivative behavior becomes critical.
Examples include:
- Automated trading systems reacting to price momentum
- Recommendation engines adapting to user engagement changes
- Control systems adjusting to environmental feedback
- Monitoring systems detecting instability or anomalies
Derivative classification training enables professionals to anticipate system behavior rather than react after failure occurs.
Linking Derivative Classification to Risk Management
Risk is often associated with rapid or unstable change. Derivatives quantify this change, and classification helps identify risky zones.
Applications in risk management include:
- Detecting accelerating losses in financial portfolios
- Identifying unstable operating regions in engineering systems
- Monitoring rapid changes in customer behavior metrics
- Flagging model instability during machine learning training
By classifying derivative behavior early, organizations can mitigate risk proactively.
Role in Feature Engineering and Model Diagnostics
In data science, features that capture rates of change often outperform raw values. Derivative classification training improves intuition for designing such features.
Examples include:
- Growth rates instead of absolute counts
- Momentum indicators instead of static prices
- Acceleration metrics instead of simple trends
Additionally, classification of gradients during model training helps diagnose issues such as slow convergence or instability.
Derivative Classification in Multivariable Environments
As systems become more complex, variables rarely operate in isolation. Multivariable derivative classification introduces additional dimensions of interpretation.
Key concepts include:
- Partial derivatives representing isolated effects
- Gradient vectors showing direction of maximum change
- Hessian matrices classifying curvature in multiple dimensions
Training in these areas prepares learners for advanced optimization and deep learning applications.
Assessment Strategies for Derivative Classification Mastery
Effective assessment goes beyond numerical correctness. High-quality evaluation focuses on explanation, justification, and interpretation.
Recommended assessment methods include:
- Graph interpretation exercises
- Scenario-based classification questions
- Error diagnosis tasks
- Real-world case analysis
Such assessments ensure that learners truly understand derivative behavior rather than relying on rote calculation.
Organizational Benefits of Derivative Classification Training
When adopted at an organizational level, this training approach delivers measurable benefits:
- Faster analytical decision cycles
- Improved model interpretability
- Reduced analytical errors
- Stronger collaboration between technical and non-technical teams
Organizations that emphasize interpretability gain a competitive advantage in complex, data-driven environments.
Alignment with Modern Data Literacy Initiatives
Data literacy initiatives aim to make analytical reasoning accessible across roles. Derivative classification training aligns naturally with this goal.
It supports:
- Intuitive understanding of trends and change
- Clear communication of analytical insights
- Shared reasoning frameworks across departments
- Reduced dependence on technical jargon
This makes derivative concepts approachable even for non-specialists.
Long-Term Relevance in an AI-Driven Future
As artificial intelligence systems become more autonomous, understanding how and why outputs change will be increasingly important. Derivative classification training equips professionals with the tools to reason about system behavior responsibly.
It contributes to:
- Explainable and trustworthy AI
- Responsible optimization practices
- Sustainable system design
- Human-centered analytics
These qualities will define the next generation of intelligent systems.
Challenges in Scaling Derivative Classification Training
Despite its benefits, scaling this training approach presents challenges:
- Learners often struggle with abstraction
- Visualization tools may be underutilized
- Overemphasis on formulas persists in traditional teaching
- Application contexts vary across industries
Addressing these challenges requires thoughtful instructional design and technology support.
Emerging Research Directions
Current research in mathematical education and AI learning systems is exploring:
- Automated feedback for derivative interpretation
- AI tutors that explain derivative behavior visually
- Integration of symbolic and numerical differentiation learning
- Assessment methods focused on reasoning rather than computation
These research directions will further enhance derivative classification training effectiveness.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Frequent errors include:
- Ignoring function context
- Misinterpreting zero derivatives
- Over-relying on formulas
Structured classification training reduces these errors by enforcing interpretation-based learning.
Advanced Learning Paths and Skill Progression
After mastering the basics, learners can progress to:
- Multivariable derivatives
- Hessian matrix classification
- Optimization in deep learning
Each stage builds upon earlier derivative classification skills.
Practical Case Study
A retail analytics company used derivative classification training to optimize pricing strategies. By classifying demand curve derivatives, the company improved profit margins through precise elasticity analysis.
This demonstrates real-world impact beyond academic theory.
Best Practices for Long-Term Mastery
- Practice with real datasets
- Use visualization consistently
- Combine theory with application
- Review classification rules regularly
These practices ensure sustainable skill development.
Future Scope of Derivative-Based Classification
As AI systems become more complex, interpretability will matter more. Classification-based derivative understanding will play a key role in explainable AI and responsible model design.
Conclusion
Derivative classification training represents a powerful evolution in how derivatives are taught, understood, and applied. Rather than focusing solely on calculation, this structured approach emphasizes interpretation, behavior analysis, and real-world relevance.
By classifying derivatives based on sign, order, and contextual meaning, learners develop deeper intuition and stronger analytical skills. These skills are essential in modern fields such as data science, machine learning, economics, engineering, and artificial intelligence.
As systems become more data-driven and optimization-focused, the ability to interpret change accurately will remain a core competency. Derivative classification training bridges the gap between mathematical theory and practical decision-making, making it a critical component of modern analytical education.
Through consistent practice, visualization, and application-driven learning, individuals and organizations can unlock the full potential of derivatives—not just as mathematical tools, but as engines of insight and innovation.
FAQ’s
What is derivative classification training?
Derivative classification training teaches analysts how to assign correct classification levels to data derived from existing information, ensuring security, compliance, and proper handling of sensitive or regulated data.
What are the three required elements on a derivatively classified document?
A derivatively classified document must include the source document or classification guidance, the overall classification level, and the declassification instructions (or date/event) to ensure proper security handling.
What is derivative analysis?
Derivative analysis is the process of examining data or information derived from existing sources to understand patterns, implications, or classification requirements, ensuring accurate interpretation and proper use.
What are the requirements for derivative classifier training?
Derivative classifier training requires individuals to understand classification guidance, source documents, marking rules, and declassification instructions to correctly classify information derived from classified sources.
What are the 4 types of derivatives?
The four common types of derivatives are constant derivatives, power derivatives, exponential & logarithmic derivatives, and trigonometric derivatives, which describe how different mathematical functions change.