Introduction
Welcome to ‘7 Key Strategies in Master Data Management: Unifying Enterprise Data,’ a comprehensive guide to mastering the art of Master Data Management (MDM). This in-depth exploration delves into essential strategies for unifying enterprise data, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and accessibility across an organization. MDM is more than just a technology; it’s a crucial business strategy pivotal in data governance, data quality, and overall business efficiency.
Understanding Master Data Management
Master Data Management (MDM) is a methodical approach to managing an organization’s critical data. It focuses on creating a single, authoritative source of truth for all master data within an enterprise, essential for businesses dealing with large volumes of data across different departments and systems. MDM ensures everyone in the organization has access to the same, accurate, and up-to-date information, reducing errors, improving efficiency, and supporting strategic initiatives.
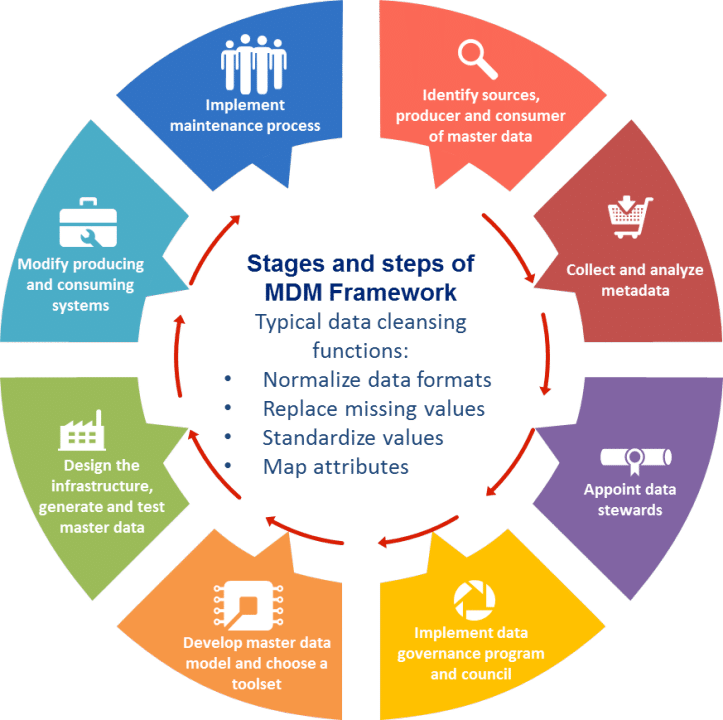
Facilitating Cross-Departmental Collaboration and Consistency
- Beyond centralizing data, Master Data Management plays a crucial role in facilitating cross-departmental collaboration and consistency within an organization. By providing a unified view of master data, MDM breaks down silos between different departments, ensuring that all teams are working with the same data set. This harmonization is particularly vital for large organizations where different departments may have their own systems and data repositories. MDM ensures that whether it’s marketing, sales, finance, or operations, every department bases its strategies and decisions on a consistent set of data, leading to more cohesive and aligned organizational efforts.
Supporting Regulatory Compliance and Data Governance
- MDM also significantly contributes to regulatory compliance and data governance. In an environment with stringent data regulations, having a centralized system for managing master data helps ensure compliance with various legal standards, including data privacy laws like GDPR or HIPAA. MDM systems can enforce consistent data handling and storage practices, making it easier to adhere to these regulations. Additionally, with the increasing focus on data governance, MDM provides the framework for defining and enforcing policies and procedures around data usage, access, and quality, ensuring that data is not only used effectively but also responsibly and ethically.
The Importance of Master Data Management in Modern Business
MDM has become an indispensable part of modern business strategy. In an era where data drives decisions, MDM provides the foundation for high-quality, reliable data. It’s crucial for businesses aiming to leverage data for competitive advantage, ensuring consistency and availability of critical business information across the organization.
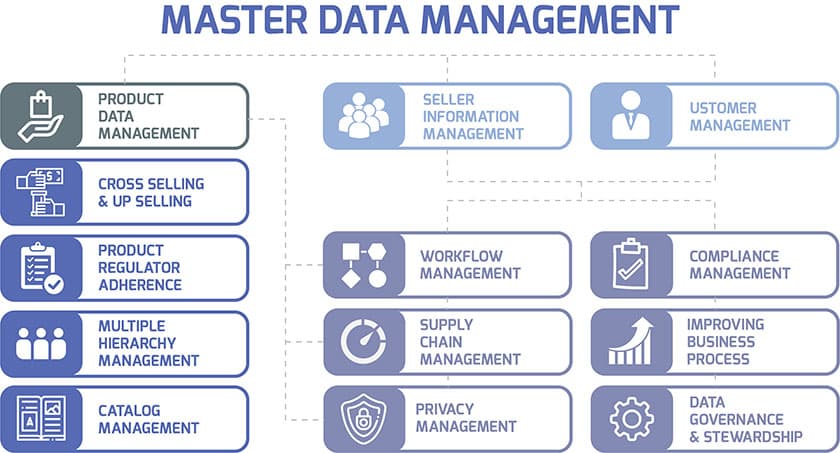
1. Data Governance and Stewardship
- Implementing robust data governance and stewardship is vital in MDM. This involves establishing clear policies, roles, and responsibilities for managing master data, and ensuring data quality and compliance.
- Data stewardship ensures ongoing management and maintenance of master data, involving regular audits, updates, and validation to maintain data integrity.
2. Data Quality Management
- Ensuring high data quality is a cornerstone of effective MDM. This includes processes for data cleansing, de-duplication, and validation to ensure the master data is accurate and reliable.
- Regular data quality assessments help identify and rectify issues, maintaining the integrity of the master data over time.
3. Integration of Data Sources
- MDM requires integrating various data sources to create a unified view of master data. This involves consolidating data from disparate systems, databases, and applications.
- Effective integration tools and technologies are essential for seamless data consolidation, ensuring that data remains synchronized and up-to-date across systems.
4. Scalable and Flexible Master Data Management Architecture
- Developing a scalable and flexible MDM architecture is crucial to accommodate growing data volumes and evolving business needs.
- The architecture should support easy integration of new data sources, adapt to changing data models, and scale to handle increased data loads.
5. Master Data Security and Compliance
- Ensuring the security and compliance of master data is paramount. This involves implementing robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR is essential, requiring processes for data privacy, consent management, and audit trails.
6. User Training and Adoption
- Successful MDM implementation requires user training and adoption. Stakeholders across the organization should be trained on MDM processes, tools, and best practices.
- Encouraging user adoption through training, support, and demonstrating the value of MDM is key to its success.
7. Continuous Monitoring and Improvement
- MDM is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and improvement. Regular reviews and updates to the MDM strategy ensure it remains aligned with business objectives and industry best practices.
- Leveraging analytics and feedback to refine MDM processes and strategies is crucial for long-term success.
Leveraging Technology in MDM
- Embracing the latest technology trends like AI and machine learning can significantly enhance MDM processes. These technologies can automate data management tasks, improve data quality, and provide predictive insights.
- Cloud-based Master Data Management solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, making them an attractive option for many organizations.
Blockchain Integration for Enhanced Security and Transparency
The integration of blockchain technology in MDM presents a groundbreaking approach to ensuring data security and transparency. Blockchain’s decentralized nature allows for the creation of an immutable ledger of master data transactions, providing an additional layer of security against tampering and fraud.
This technology can revolutionize how master data is tracked and audited, offering unparalleled transparency in data transactions. For industries where data authenticity and traceability are paramount, such as healthcare and finance, blockchain integration in MDM can significantly enhance trust and compliance.
IoT and Master Data Management Convergence for Real-Time Data Management
The convergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) with Master Data Management opens new avenues for real-time data collection and analysis. IoT devices generate vast amounts of data that, when effectively managed through MDM systems, can provide real-time insights and operational intelligence.
This integration allows organizations to respond swiftly to changing conditions, optimize processes, and enhance decision-making. For instance, in manufacturing, IoT sensors can feed data directly into MDM systems, enabling real-time monitoring and adjustments in production processes, leading to increased efficiency and reduced downtime.
MDM and Big Data Analytics
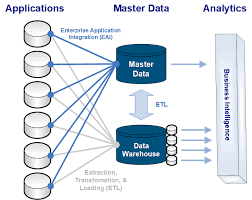
Enhancing Predictive Analytics and Decision Intelligence
- The synergy between MDM and big data analytics extends significantly into the realms of predictive analytics and decision intelligence. By providing a clean, unified, and reliable dataset, MDM lays the groundwork for sophisticated predictive models and analytics. These models can analyze trends, forecast future scenarios, and provide actionable intelligence that can guide strategic business decisions.
- For instance, in retail, MDM-driven big data analytics can predict purchasing trends, optimize inventory management, and personalize customer experiences. This integration not only streamlines operational processes but also helps in identifying new market opportunities and predicting risks, thereby giving businesses a competitive edge in a data-driven marketplace.
- MDM plays a crucial role in the realm of big data analytics. By ensuring the quality and consistency of master data, MDM enables more accurate and reliable big data analysis.
- Integrating MDM with big data tools and platforms can unlock deeper insights and drive more informed business decisions.
Essential Components of a Master Data Management Strategy for an Enterprise
A successful Master Data Management strategy relies on the presence of core components that work seamlessly to standardize, govern, and enhance enterprise data. These components form the backbone of any sustainable MDM framework:
1. Master Data Governance
Well-defined data ownership, accountability, and governance frameworks ensure consistent management and usage of data across systems and departments.
2. Data Quality and Standardization
MDM strategies must include quality rules, validation frameworks, and cleansing mechanisms to maintain accuracy and eliminate redundancies.
3. Data Integration and Interoperability
Seamless integration between CRM, ERP, finance, HR, and external data sources is essential. MDM platforms should support APIs, middleware, data ingestion pipelines, and batch + real-time synchronization.
4. Metadata and Reference Data Management
Maintaining metadata dictionaries and standard reference values ensures uniform classification, reduces conflicts, and improves discoverability of information.
5. Security, Compliance & Risk Framework
Role-based access controls, encryption policies, compliance mapping (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS), and audit trails are necessary to protect sensitive master data.
Organizational and Cultural Aspects of Efficient Master Data Management Strategy
MDM is not only a technology decision—it is a cultural transformation within the enterprise.
Leadership Sponsorship
Executive endorsement enables funding, cross-department alignment, and policy enforcement.
Data-driven Culture
Encouraging employees to value accuracy, governance discipline, and responsible data consumption fosters sustainable MDM adoption.
Collaborative Workflows
MDM improves value when departments collaborate rather than operate in silos. Shared KPIs, joint review boards, and transparent reporting strengthen alignment.
Change Management
Clear communication, workshops, and showcasing early wins build confidence and accelerate organizational acceptance of MDM practices.
Developing a Master Data Management Strategy
Creating a successful MDM strategy follows a structured planning lifecycle:
- Assess Data Maturity & Landscape
Audit current systems, define data issues, and identify integration points. - Define MDM Scope & Objectives
Decide what master data entities to cover first (customer, supplier, product, finance, etc.). - Establish Governance Roles & Policies
Form data stewardship teams, define data ownership rules, and set quality KPIs. - Select the MDM Technology Stack
Choose on-premise, cloud, or hybrid platforms based on scalability, integration capabilities, and cost. - Implement in Phases
Adopt an iterative rollout—starting small, validating, then scaling. - Monitor, Measure, Improve
Track data accuracy, latency, usage trends, adoption metrics, and continuously refine.
Master Data Management Strategy Template (Ready to Use)
| Section | Description |
| Vision & Business Objectives | Define what the enterprise wants to achieve with MDM. |
| Master Data Domains | Customer / Product / Employee / Vendor / Asset / Location, etc. |
| Governance Structure | Roles: Data owners, Stewards, Custodians, Governance Council. |
| Data Quality Standards | Validation rules, cleansing policies, data completeness thresholds. |
| Technology Framework | MDM system, ETL tools, storage, integration architecture. |
| Security & Compliance | Access control, encryption, risk management guidelines. |
| Implementation Roadmap | Phases, timelines, milestones, budget allocation. |
| Monitoring & KPIs | Accuracy %, duplicate reduction, data quality score, adoption rate. |
This template can be converted into a business-ready document or framework for MDM execution.
MDM Strategy Tools and Technology Infrastructure Specifics
Core Platforms for MDM Execution
- Informatica MDM
- SAP Master Data Governance
- IBM InfoSphere MDM
- Oracle Customer Hub
- Semarchy xDM
- Microsoft Purview
Supporting Infrastructure
| Category | Tools / Technologies |
| ETL / Pipeline | Talend, Apache Airflow, SSIS, Fivetran |
| Data Quality | Collibra, Ataccama, Trifacta, Precisely |
| Integration Layer | API Gateways, ESB, Kafka, MuleSoft |
| Cloud Platforms | AWS Glue, Azure Data Factory, GCP Data Fusion |
| Analytics Layer | Power BI, Qlik Sense, Tableau |
A modern MDM ecosystem requires elasticity, real-time streaming support, multi-domain management, and AI-assisted quality improvement.
Challenges in MDM Implementation and Approaches to Their Mitigation
| Challenge | Root Cause | Mitigation Approach |
| Data Silos & Fragmented Systems | Multiple independent sources | Enterprise-wide integration + standardization layer |
| Low Stakeholder Adoption | Resistance to change | Robust training, communication & showcasing ROI |
| Poor Data Quality | Legacy errors, duplication | Automated cleansing, profiling, rule-based validation |
| Limited Governance Discipline | Undefined ownership | Appoint data stewards & governance council |
| Scaling Difficulties | Rigid architecture | Cloud-first, modular & API-driven MDM frameworks |
| Compliance Risk | Uncontrolled access | Policy-based security + audit traceability |
Proactive planning and phased implementation help minimize operational disruption.
Why Choose SPD Technology for Data Quality Management Solutions?
SPD Technology stands out as a trusted partner for enterprises seeking scalable, future-ready data quality and MDM solutions. Their frameworks emphasize:
✔ AI-Enhanced Data Quality Workflows
Automated cleansing, de-duplication, anomaly detection, and predictive data enrichment.
✔ Enterprise-Grade Integration
Seamless interoperability with ERPs, CRMs, cloud systems, and legacy applications.
✔ Customizable, Scalable Architecture
Solutions tailored to business complexity, growth, and multi-domain expansion.
✔ Compliance-First Governance Approach
Built-in regulatory controls for privacy, auditability, and secure master data handling.
✔ End-to-End MDM Implementation Support
From strategic planning and tool selection to deployment, adoption, and long-term optimization.
Selecting SPD Technology gives organizations a competitive edge by unlocking reliable, consistent, and intelligent master data at scale.
Conclusion
Master Data Management is a strategic imperative in today’s data-driven business landscape. By implementing these seven key strategies and embracing technological advancements, organizations can effectively manage their master data, unlocking its full potential to drive better decision-making, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage. As data continues to be a critical asset, MDM will play an increasingly important role in shaping business strategies and outcomes.
FAQ’s
What is the master data management strategy?
A master data management strategy is a structured approach to organizing, integrating, and maintaining core business data, ensuring accuracy, consistency, and accessibility across the entire enterprise.
What are the 4 types of MDM implementation styles?
The four MDM implementation styles are Registry, Consolidation, Coexistence, and Transactional Hub, each offering different levels of data integration, synchronization, and control to manage enterprise master data effectively.
What are the 5 C’s of data management?
The 5 C’s of data management are Consistency, Completeness, Cleanliness, Compliance, and Connectivity, which together ensure data remains accurate, reliable, secure, and well-integrated across an organization.
What is master data harmonization?
Master data harmonization is the process of aligning, standardizing, and unifying data from different sources to create one accurate, consistent version of core business information across the enterprise.
What are the three major activities of MDM?
The three major activities of MDM are data integration, data governance, and data stewardship, which ensure master data is unified, controlled, and maintained accurately across the organization.