Technology has progressed so rapidly that intelligent systems are now capable of performing tasks once thought to be purely human-driven. Much of this progress can be credited to artificial learning, a field that drives modern automation, prediction systems, virtual assistants, and numerous digital innovations across industries. In this guide, the goal is to explore artificial learning in depth without overwhelming readers, while ensuring a technically sound, SEO-optimized structure.
Understanding the Concept of Artificial Learning
Artificial learning is a branch of artificial intelligence where systems are developed to mimic how humans learn from experience. Instead of being explicitly programmed for every task, these systems analyze patterns, identify relationships, and improve automatically as more data becomes available.
Key characteristics include:
- The ability to adapt using experience
- Pattern recognition from structured or unstructured data
- Continuous self-improvement
- Reduced reliance on manual programming
- The use of advanced computational models
Artificial learning helps machines navigate complex real-world environments, from speech recognition to autonomous systems.
Evolution of Machine Intelligence and Artificial Learning
The transformation from traditional deterministic programming to flexible, learning-based systems took decades. The progression can be understood through several stages:
Early Computational Models
Basic algorithms followed strict rule-based instructions. They lacked adaptability and were suitable only for narrow tasks.
Rise of Statistical Learning
The introduction of probability-based modeling helped systems understand uncertainty instead of working with fixed instructions.
Neural Networks and Deep Architectures
Modern artificial learning gained momentum when multi-layered neural systems started performing vision, speech, and text-generation tasks with high accuracy.
Advancements in Hardware
GPUs, TPUs, and cloud-based compute clusters made large-scale model training feasible for real-world environments.
Today, artificial learning supports adaptive healthcare solutions, large language models, intelligent robots, automated trading systems, and much more.
How Artificial Learning Works
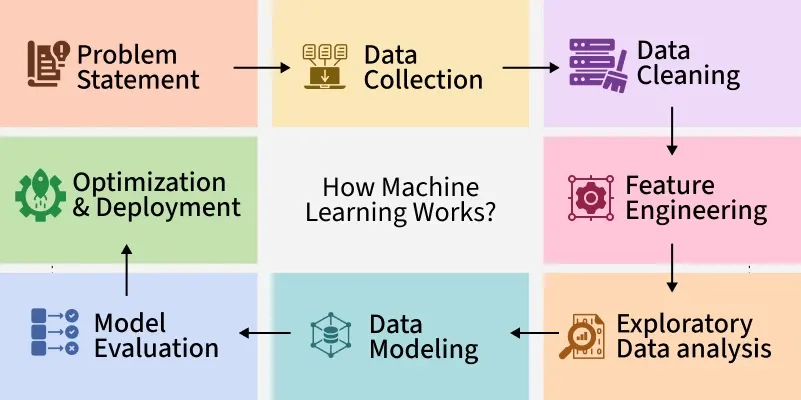
Artificial learning works through a cycle that mimics human learning and cognitive development. The standard learning pipeline includes:
- Data Collection
Raw data from sensors, logs, transactions, images, videos, or text. - Data Processing and Cleaning
Eliminating inconsistencies, duplicates, missing values, and noise. - Feature Engineering
Selecting the characteristics that help improve model accuracy. - Model Training
Feeding the cleaned data into algorithms that detect patterns. - Model Evaluation
Checking accuracy, precision, recall, and overall performance. - Model Optimization
Improving efficiency, eliminating bias, refining parameters. - Deployment
Making the system available for end users or business operations.
This pipeline ensures the artificial learning system adapts over time and improves as more data becomes available.
Types of Artificial Learning
Artificial learning is broadly classified into multiple categories based on the problem structure and type of data available.
1. Supervised Learning
The system learns using labeled datasets. Each input is paired with an expected output.
Examples:
- Fraud detection in financial transactions
- Customer churn prediction
- Email spam classification
2. Unsupervised Learning
Models operate without labeled output. They explore patterns on their own.
Examples:
- Customer segmentation
- Market basket analysis
- Anomaly detection
3. Semi-Supervised Learning
Uses a mix of labeled and unlabeled data. Useful when labeling large datasets is expensive.
Example:
- Identifying disease patterns from medical imaging
4. Reinforcement Learning
Learning is based on reward and punishment. The system interacts with its environment and improves from feedback.
Real-life example:
- Robotics navigation
5. Deep Learning
Advanced neural architectures capable of understanding complex hierarchical patterns.
Example:
- Image classification
- Natural language understanding
Core Components That Power Artificial Learning
Artificial learning involves well-structured components that strengthen model performance.
1. Data
High-quality structured or unstructured data drives the accuracy of artificial learning.
2. Algorithms
Mathematical models such as neural networks, decision trees, and clustering methods form the backbone.
3. Feature Sets
Better features enhance learning efficiency.
4. Compute Infrastructure
Cloud compute platforms, GPUs, and distributed frameworks power model training.
5. Feedback Mechanisms
Allow continuous improvement and learning.
Mathematical Foundations Behind Artificial Learning
Understanding the mathematics behind artificial learning helps establish credibility and technical depth.
Core mathematical pillars:
- Linear Algebra:
Used in neural networks for operations like matrix multiplication, tensor decomposition, and weight transformations. - Calculus (Differentiation & Gradient Descent):
Essential for optimizing model functions through backpropagation. - Probability Theory & Statistics:
Probability distributions, likelihood functions, Bayesian inference, and error estimations are central to prediction models. - Optimization Algorithms:
Techniques such as Adam, RMSProp, and SGD ensure models converge efficiently.
These foundations help machines quantify uncertainty, minimize errors, and adjust themselves during training.
Role of Feature Engineering in Artificial Learning
Artificial learning systems perform best when the input features are correctly engineered.
Key feature engineering strategies:
- Scaling and normalization
- Dimensionality reduction (PCA, t-SNE)
- Feature selection via statistical tests
- Encoding of categorical variables
- Creation of domain-specific derived features
Example:
In supply chain demand forecasting, engineered features like holiday influence, weather index, and promotional history significantly improve model accuracy.
Model Interpretability and Explainable Artificial Learning
As artificial learning becomes more embedded in critical systems, interpretability has become crucial.
Techniques for Explainability:
- SHAP (SHapley Additive Explanations)
- LIME (Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations)
- Feature importance ranking
- Partial dependence plots
- Counterfactual explanations
Practical use-case:
A healthcare provider uses SHAP to explain why a model predicted a high risk of cardiac arrest, allowing doctors to trust machine-generated recommendations.
Artificial Learning in Autonomous Decision-Making Systems
Autonomous systems rely heavily on artificial learning to simulate human-like decision structures.
Examples include:
- Self-driving cars analyzing sensor inputs
- Delivery drones optimizing flight paths
- Industrial robots adapting to dynamic environments
These systems require continuous real-time learning, which is supported by reinforcement learning and deep neural architectures.
Artificial Learning in Cybersecurity
As cyberattacks increase, artificial learning systems are becoming essential.
Application areas:
- Threat detection through pattern deviation
- Behavioral biometrics
- Malware classification
- Intrusion detection systems
- Authentication systems using anomaly detection
Example:
A global IT company uses artificial learning to analyze billions of log entries daily, detecting unauthorized access attempts in real-time.
Large-Scale Artificial Learning Using Distributed Computing
Modern training often requires powerful distributed frameworks.
Technologies enabling large-scale learning:
- Apache Spark MLlib
- TensorFlow distributed training
- PyTorch distributed data parallel
- Kubernetes for model orchestration
- Federated learning for decentralized data training
Federated learning is particularly valuable for industries where data privacy is essential, such as healthcare and finance.
Artificial Learning for Natural Language Processing
NLP relies heavily on hierarchical artificial learning systems.
Key areas:
- Language modeling
- Sentiment analysis
- Named entity recognition
- Document summarization
- Speech-to-text systems
Example:
Customer support centers use artificial learning-powered chatbots to respond to customer issues in real-time and reduce human workload.
Ethical Considerations and Bias in Artificial Learning
Artificial learning systems must be governed responsibly.
Major bias contributors:
- Skewed datasets
- Non-representative sampling
- Historical human bias encoded into data
- Poor labeling consistency
- Cultural or demographic imbalance
Mitigation strategies:
- Fairness-aware algorithms
- Diverse datasets
- Regular bias audits
- Transparent reporting
Artificial Learning Pipelines with MLOps
MLOps ensures continuous integration and continuous deployment for artificial learning.
MLOps components:
- Automated data pipelines
- Model versioning
- Monitoring and retraining
- Model registry
- Deployment automation
Example:
E-commerce platforms retrain recommendation models weekly using automated MLOps pipelines to reflect new buying behaviors.
Artificial Learning and Edge Computing
Running artificial learning models on edge devices reduces latency and enables offline processing.
Edge-enabled devices:
- Smart cameras
- Mobile phones
- IoT sensors
- Industrial machines
Example:
A smart manufacturing plant uses artificial learning at the edge to detect product defects instantly without needing cloud communication.
Artificial Learning in Generative Systems
Generative artificial learning has reshaped media creation.
Technologies:
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs)
- Variational autoencoders (VAEs)
- Transformer-based generative models
Applications include:
- Image creation
- Audio synthesis
- Text generation
- Video enhancement
Advanced Use of Artificial Learning in Climate Science
Environmental researchers use artificial learning to tackle global challenges.
Use cases:
- Predicting severe weather patterns
- Monitoring deforestation through satellite images
- Carbon emission analysis
- Ocean temperature modeling
This contributes to sustainability and environmental protection efforts.
Artificial Learning in Scientific Discovery
Artificial learning is now helping accelerate breakthroughs in fields like physics, chemistry, and biology.
Examples:
- Protein structure prediction
- Drug molecule discovery
- Material science simulations
- Physics experiment optimizations
Artificial learning shortens analysis cycles that traditionally took months to years.
Economic Impact of Artificial Learning
Artificial learning is reshaping global economies.
Key impacts:
- Automation of repetitive tasks
- New AI-centric industries
- Higher demand for data-centric job roles
- Increased productivity and operational efficiency
Major companies like Amazon, Google, and Tesla rely heavily on artificial learning for scaling operations and building competitive advantages.
Real-Time Applications Transforming Industries
Below are practical scenarios where artificial learning is reshaping systems globally.
Healthcare
Artificial learning helps predict disease outbreaks, assist radiologists with diagnostics, and personalize treatment plans.
Retail
Real-time recommendation engines personalize user shopping experiences.
For example, e-commerce platforms recommend items based on browsing behavior.
Finance
Risk modeling, fraud detection, market forecasting, and trading bots rely on adaptive learning.
Manufacturing
Predictive maintenance prevents machinery failures and reduces operational downtime.
Transport
Navigation systems learn traffic patterns to optimize routing dynamically.
Artificial Learning in Data Engineering and Analytics
Artificial learning plays a strategic role in analytics as companies generate massive datasets daily. It helps identify trends that are not visible through manual inspection.
Key contributions include:
- Efficient handling of high-volume data
- Predictive insights for business decisions
- Intelligent dashboards
- Enhanced data pipelines
- Automated reporting systems
Example:
A logistics company uses artificial learning to analyze real-time sensor logs from delivery vehicles. This helps optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and increase delivery efficiency.
Challenges Limiting Artificial Learning
1. Data Scarcity or Poor Data Quality
Models fail if they are trained on inaccurate or inconsistent datasets.
2. Overfitting
When a model learns too much from training data and performs poorly on new datasets.
3. Ethical Concerns
Biases in datasets can lead to unfair outcomes.
4. High Compute Requirements
Advanced models require powerful hardware.
5. Interpretability Issues
Deep architectures behave like black boxes, making it difficult to understand internal decision mechanisms.
Future Trends Shaping Artificial Learning
Artificial learning continues to evolve with innovations such as:
- Self-supervised learning
- Quantum-powered learning models
- Fully autonomous data preparation pipelines
- Explainable artificial intelligence
- Automated machine intelligence systems
These advancements will reshape industries through smarter automation.
Real-World Case Studies and Practical Scenarios
Case Study: Retail Sales Forecasting
A fashion retail chain integrated artificial learning with historical sales data, customer behavior, and seasonal trends.
Outcome: Increased demand prediction accuracy and reduced inventory wastage.
Case Study: Fraud Detection
A multinational bank used pattern-recognition models to detect abnormal fund transfers in real-time.
Outcome: Reduction in fraudulent activities and improved customer trust.
Case Study: Predictive Maintenance
A global manufacturing company used artificial learning to analyze vibration signals and temperature patterns in machinery.
Outcome: Lower breakdowns and efficient production operations.
Best Practices for Implementing Artificial Learning
Below are techniques that improve the success rate of artificial learning systems.
1. Start with Clean and Representative Data
Quality matters more than quantity.
2. Build Explainable Frameworks
Helps ensure trust and transparency.
3. Use the Right Algorithm
Different problems require different algorithm families.
4. Continuously Monitor Performance
Retraining models prevents outdated predictions.
5. Maintain Data Security
Ensure compliance and protect sensitive information.
External Resources for Further Learning
- Stanford CS229 Machine Learning course
- Google AI documentation
- MIT OpenCourseWare on AI theory
- Research papers from top universities
These provide deep insights into artificial learning and modern research efforts.
Conclusion
Artificial learning is transforming industries, reshaping digital ecosystems, and driving intelligent automation across every business sector. As data continues to grow and compute systems evolve, artificial learning will become the foundation of next-generation applications. The combination of structured pipelines, advanced algorithms, high-quality datasets, and transparent governance will unlock new opportunities for innovation and large-scale adoption of artificial intelligent systems.
FAQ’s
What is artificial learning?
Artificial learning refers to the process by which machines learn patterns from data using algorithms, enabling them to make predictions, decisions, or perform tasks without being explicitly programmed.
How does artificial learning differ from machine learning?
Artificial learning differs from machine learning by focusing on creating self-evolving, human-like learning systems, while machine learning relies on data-driven algorithms that learn from patterns without true cognitive adaptation.
Why is artificial learning important for modern intelligent systems?
Artificial learning is important for modern intelligent systems because it enables them to continuously adapt, self-improve, and make autonomous decisions, resulting in smarter, more efficient, and future-ready technologies.
What are the main types of artificial learning?
The main types of artificial learning include supervised learning, unsupervised learning, reinforcement learning, and deep learning—each designed to help systems learn patterns, make decisions, or improve through experience.
What industries benefit the most from artificial learning?
Industries like healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail, and transportation benefit most from artificial learning, using it to improve decision-making, automate processes, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.



