Artificial intelligence has become an essential part of modern workflows, from creative content generation to business automation. At the center of this transformation is a rapidly growing expert role known as the ai prompt engineer. This specialized professional shapes the behavior, accuracy, and efficiency of AI systems using well-structured instructions known as prompts.
While traditional software development once dominated automation, prompt engineering has created a new pathway for people to take control of AI-powered tasks with unprecedented ease. Instead of writing long lines of code, an ai prompt engineer designs language-based instructions that guide AI models to produce accurate, actionable results.
What Is an AI Prompt Engineer?
An ai prompt engineer is a professional who creates, tests, and optimizes prompts to help AI models generate reliable and context-aware outputs.
These prompts act as the interface between human intent and machine intelligence.
Key responsibilities:
- Designing structured prompts for various tasks
- Analyzing model outputs and improving them
- Understanding model behavior and limitations
- Creating automated workflows using AI tools
- Collaborating with developers, content teams, and analysts
- Testing and refining prompts for different use cases
Prompt engineers bridge the gap between human creativity and machine logic.
Why the Role of an AI Prompt Engineer Is Growing Rapidly
The rise of large language models and generative AI has dramatically changed how organizations work. Instead of depending solely on traditional programming, businesses rely heavily on prompt-driven AI systems.
Reasons behind rapid demand:
- AI adoption in business operations
- Need for optimized and reliable AI outputs
- Increased use of AI for writing, coding, analysis, and automation
- Companies wanting professionals who understand how to “speak” to AI
- Growth of no-code tools that function through prompts
- Efficiency improvements through prompt-powered workflows
According to emerging industry reports, companies using prompt engineering are reducing content creation time by up to 70% and improving automation accuracy by 40%, highlighting why prompt engineering is now seen as a critical skill.
Understanding AI Prompt Engineering
AI prompt engineering is the practice of crafting text-based instructions to guide AI systems. It requires a mix of creativity, logic, linguistic understanding, and problem-solving.
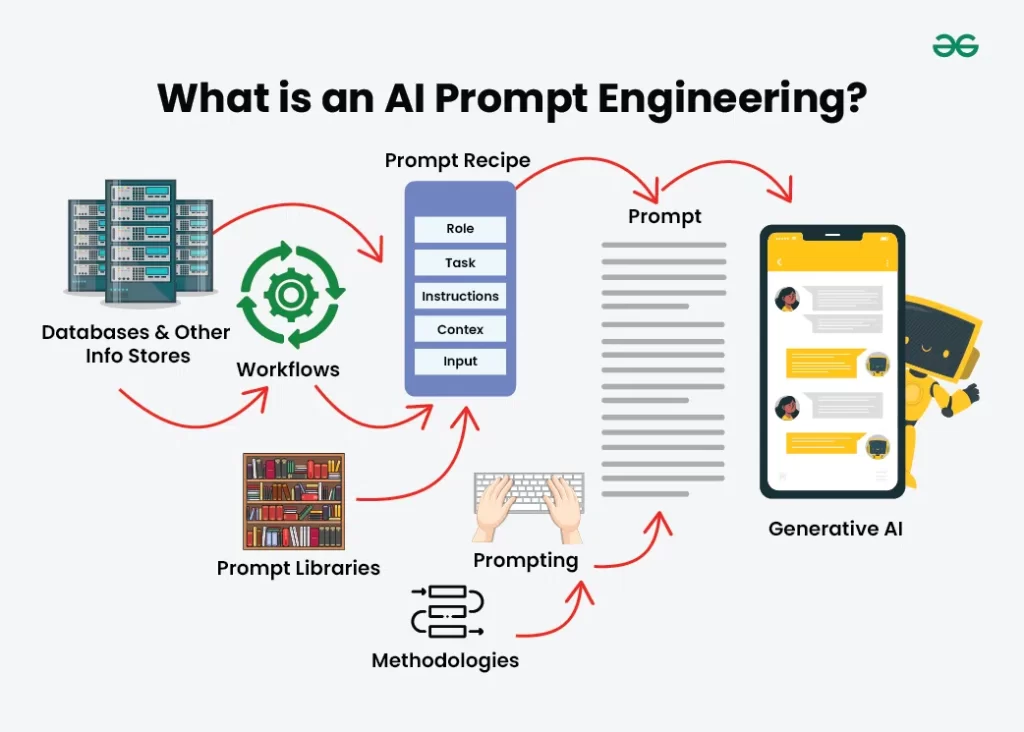
The structure of a well-designed prompt:
- Context: Background information
- Intent: What the user wants
- Constraints: Limits or guidelines
- Format: The expected structure of the output
Example prompt structure:
“Write a two-paragraph explanation of renewable energy, include a comparison chart, and use simple language suitable for students.”
Prompts like this help AI produce precise, usable responses.
How AI Prompt Engineering Helps You Take Control of Digital Workflows
One of the biggest advantages of prompt engineering is the ability to take control of workflows without technical complexities. People once dependent on manual tasks or coding can now automate entire processes using natural language prompts.
Areas where control improves:
- Content creation
- Data extraction
- Business automation
- Customer support replies
- Research and summarization
- Code generation and debugging
- Report generation
Real-time Example
A marketing team automates product descriptions using a set of prompts designed by an ai prompt engineer.
Instead of writing thousands of descriptions manually, the AI generates consistent, SEO-optimized content in minutes.
Prompt engineering puts the control of complex tasks directly into the hands of the user.
Essential Skills Every AI Prompt Engineer Needs
An ai prompt engineer must combine analytical thinking with creativity.
Core skills include:
1. Understanding AI Model Behavior
Knowledge of model limitations, hallucinations, biases, and response formatting.
2. Strong Linguistic Skills
Precise language produces precise outputs.
3. Data Interpretation
Engineers must analyze data-driven outputs for accuracy.
4. Problem-Solving Ability
Debugging prompts is similar to debugging code.
5. Domain Knowledge
Examples: marketing, finance, health, education, analytics.
6. Tool Awareness
Familiarity with:
- ChatGPT
- Claude AI
- Gemini
- Jasper
- Perplexity
- Midjourney
- Hugging Face tools
7. Testing and Optimization Techniques
Iterative improvement is essential to producing reliable AI behavior.
Evolution of Prompt Engineering: From Simple Commands to Complex Instruction Design
Prompt engineering has evolved rapidly:
- Early stage (Rule-based AI): Prompts resembled commands written for chatbots with predefined flows.
- AI Language Model stage: LLMs like GPT, Claude, Gemini and Llama turned prompts into dynamic instructions, requiring creativity and problem-solving.
- Advanced stage (Agentic AI): Prompts now define multi-step workflows, tool usage, API calling, and reasoning patterns, enabling machines to complete tasks autonomously.
This helps readers understand why the role of an AI prompt engineer is now essential in modern tech teams.
Real-Time Use Case: How Big Companies Are Hiring Prompt Engineers
You can add examples like:
- OpenAI’s Prompt Engineer job offering more than $250k salary for designing prompt libraries.
- Google DeepMind uses prompt engineers to improve reasoning patterns in agentic systems.
- E-commerce companies use prompt engineers to generate personalized product descriptions.
- Healthcare startups use them for summarizing medical research safely.
This strengthens the real-world relevance.
Detailed Workflow of an AI Prompt Engineer (Step-by-Step)
Provide a full structured workflow, such as:
- Understanding user intent
- Designing prompt structure
- Choosing examples and constraints
- Adding relevant context
- Running iterative prompt tests
- Evaluating responses using quality benchmarks
- Creating a reusable prompt library
- Deploying prompts inside applications
- Monitoring performance
- Updating prompts with new model versions
This section increases the practical depth of the blog.
Explain the Concept of “Prompt Patterns” with Examples
Include advanced prompt patterns like:
- Few-shot prompting
- Chain-of-thought prompting
- ReAct prompting (Reason + Act)
- Self-critique prompting
- Persona-based prompting
- Task decomposition prompting
- Tree-of-thought prompting
Explain each with short examples.
Section About AI Prompt Engineers in Agentic Systems
Since the blog title references control/agentic behavior, this is vital.
Cover:
- How prompt engineers design autonomous agents
- How agents break tasks into smaller units
- The role of prompt instructions in enabling tool usage, browsing, coding, file handling, system operations
- Safety challenges when AI executes system-level tasks
- Why human oversight is mandatory even with advanced agentic AI
A Full Case Study: Prompt Engineering in a Real AI Project
You can include a detailed case study such as:
Case Study: Building an AI Customer Support Agent
Explain:
- Initial dataset and user queries
- How prompts were constructed
- How system prompts were optimized
- How hallucinations were reduced
- Final performance improvement (accuracy, response time, etc.)
Real case studies improve credibility.
Certifications & Courses to Become an AI Prompt Engineer
Add a resource section like:
- OpenAI learning paths
- Coursera Prompt Engineering Specialization
- DeepLearning.AI courses
- Udemy advanced prompt engineering modules
- Google Gemini prompt engineering resources
This helps readers who want to pursue a career.
Tools Used by Prompt Engineers
Useful tools include:
- LLM playgrounds (OpenAI Playground, Anthropic Console)
- Prompt optimization tools (PromptLayer, LangSmith)
- Vector databases (Pinecone, Chroma)
- Code assistants (GitHub Copilot, Cursor)
- Deployment frameworks (LangChain, LlamaIndex)
Each tool can have a short description.
Trends Section: Future of AI Prompt Engineering
Cover trends like:
- Automated prompt optimization
- Machine-generated prompts
- Prompt A/B testing tools built into AI systems
- Decline of manual prompting as AI models become context-aware
- Rise of multi-agent prompt orchestration
Compliance & Safety Section (Very Important)
Include discussion on:
- Bias prevention
- Content safety
- Ensuring AI cannot misuse system access
- Guardrails for agentic systems
- Ethical constraints prompt engineers must follow
This will make the blog more authoritative and responsible.
Visuals / Media Suggestions
To meet SEO requirements:
- Flowchart of prompt engineering workflow
- Screenshot of an AI playground
- Diagram of prompt structure
- Table comparing prompt types
- Embedded video explaining prompt engineering
These enhance readability and SEO.
Checklist: Daily Responsibilities of an AI Prompt Engineer
Example points:
- Designing high-precision prompts
- Auditing AI behavior
- Testing variations
- Documenting workflows
- Ensuring output consistency
- Collaborating with developers & data teams
- Using analytics to track performance
Readers appreciate workflow breakdowns.
Advanced Real-Time Examples for Each Section
For example:
- How a travel website uses prompt engineering to generate personalized itineraries
- How an HR department uses prompts to screen resumes
- How coding agents build full applications using structured prompts
- How finance companies use prompts for fraud detection summaries
The more practical, the better.
Real-World Use Cases of Prompt Engineering
A. E-Commerce
Automated product titles, bullet points, descriptions, and comparison tables.
B. Healthcare
Generating patient-friendly medical explanations
(Safely reviewed by professionals before use).
C. Software Development
AI-assisted code generation, documentation, and debugging.
D. Education
Lesson plans, quizzes, study notes, grading assistance.
E. Business Operations
Writing emails, preparing reports, drafting presentations.
Real-time Example
A global consulting firm uses prompt engineering to summarize client data and generate insights, saving hours of analyst work daily.
Frameworks and Techniques Used by AI Prompt Engineers
Popular frameworks include:
1. The CLEAR Framework
- Context
- Logic
- Examples
- Action
- Review
2. Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Encourages the AI to explain internal reasoning.
3. Role-Based Prompting
Example: “Act as a cybersecurity analyst.”
4. Template-Driven Prompting
Standardized patterns for repeated tasks.
5. Few-Shot Prompting
Providing examples to guide the behavior of the model.
These techniques increase reliability and reduce errors.
Tools and Platforms Used in Prompt Engineering
A professional ai prompt engineer uses multiple tools:
AI Model Platforms
- OpenAI (ChatGPT)
- Anthropic Claude
- Google Gemini
- Hugging Face
Visualization Tools
- Canva
- Figma
Automation Tools
- Zapier
- Make
- Notion AI
Research Tools
- Perplexity
- Semantic Scholar
How Businesses Benefit from Hiring an AI Prompt Engineer
Benefits include:
- Higher productivity
- Lower operational costs
- Improved accuracy
- Faster content production
- Enhanced decision-making
- Streamlined workflows
- Better AI adoption
Real-time Example
A startup reduced customer support response time by 60% after implementing AI-generated templates designed by a prompt engineer.
Prompt engineering provides scalable solutions that grow with the organization.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even skilled professionals face challenges.
Common Mistakes
- Overly vague prompts
- Lack of testing
- Missing constraints
- Ignoring model limitations
- Depending only on one AI tool
Solutions
- Add clarity and structure
- Use multiple examples
- Provide formatting instructions
- Test multiple model variations
- Monitor outputs regularly
Avoiding these mistakes creates stable, predictable AI performance.
The Future of AI Prompt Engineering
The demand for ai prompt engineers is expected to increase exponentially as AI continues integrating into everyday life.
Future trends include:
- AI-native job roles
- Enterprise-level prompt libraries
- Automated prompt testing tools
- Creative and strategic AI collaboration
- Growth of AI regulation and safety frameworks
- Advanced multimodal systems using text + image + voice + video prompts
Prompt engineering will continue evolving as AI models become more intelligent and human-aligned.
Conclusion
The rise of the ai prompt engineer marks a turning point in how individuals and businesses interact with artificial intelligence. With the right skills, techniques, and understanding, professionals can take full control of digital workflows, automate complex tasks, and drive innovation across industries.
Prompt engineering empowers creativity, enhances productivity, and ensures AI systems generate reliable, meaningful outputs. As AI continues to expand, the role of the ai prompt engineer will remain critical to shaping an efficient, responsible, and intelligent digital future.
FAQ’s
What are the 7 stages of AI?
The 7 stages of AI include reactive machines, limited memory, theory of mind, self-awareness, narrow AI, general AI, and superintelligent AI, representing the progression from basic rule-based systems to highly autonomous, human-level intelligence and beyond.
What does a prompt engineer do in AI?
A prompt engineer designs, tests, and refines prompts and instructions to help AI models generate accurate, safe, and high-quality responses, ensuring the system understands user intent effectively.
What are the 5 big ideas in AI computing?
The 5 big ideas in AI computing are Perception, Representation & Reasoning, Learning, Natural Interaction, and Societal Impact, which together explain how AI understands data, learns patterns, interacts with humans, and influences the world.
What does an AI prompt engineer do?
An AI prompt engineer creates and optimizes precise prompts, workflows, and instructions to guide AI models, ensuring they produce accurate, reliable, and safe outputs across different tasks and applications.
What is prompt engineering in large language models?
Prompt engineering in large language models is the practice of crafting clear, strategic inputs to guide the model’s responses, helping it understand context better and generate more accurate, relevant, and high-quality outputs.




