Emerging technologies are reshaping the digital landscape at an unprecedented pace, making it imperative to stay informed. These groundbreaking tools and techniques are poised to revolutionize data collection, processing, and insights. Our comprehensive guide explores the key trends in emerging data technologies, empowering you with the insights needed for a data-driven future.
Emerging Technologies Driving the Data Tech Revolution
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): At the forefront of the data technology revolution is artificial intelligence. AI encompasses machine learning, natural language processing, and neural networks, enabling automated data analysis and predictive modeling. It’s poised to revolutionize data-driven decision-making by automating complex tasks and uncovering hidden patterns in data.
- Blockchain: Beyond its association with cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology offers a novel approach to data management. Its decentralized and immutable ledger system enhances data security, transparency, and traceability. This innovation finds applications in supply chain management, healthcare, and even voting systems.
- Edge Computing: Traditional cloud computing solutions have paved the way for edge computing, a paradigm shift in data processing. Edge computing processes data closer to its source, reducing latency and enabling real-time analysis. This is especially critical for applications in the Internet of Things (IoT) and autonomous systems.
- 5G Connectivity: The advent of fifth-generation (5G) wireless technology is set to revolutionize data transfer speeds. With exponentially faster bandwidth and lower latency, 5G supports emerging technologies like augmented reality and the vast expansion of IoT devices, which can now communicate seamlessly and in real-time.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing is on the horizon, promising to solve complex problems at speeds inconceivable to classical computers. By leveraging quantum bits or qubits, quantum computers can explore numerous solutions simultaneously, providing a quantum leap in data analysis capabilities. This emerging technology is poised to redefine how we tackle optimization, cryptography, and scientific simulations.
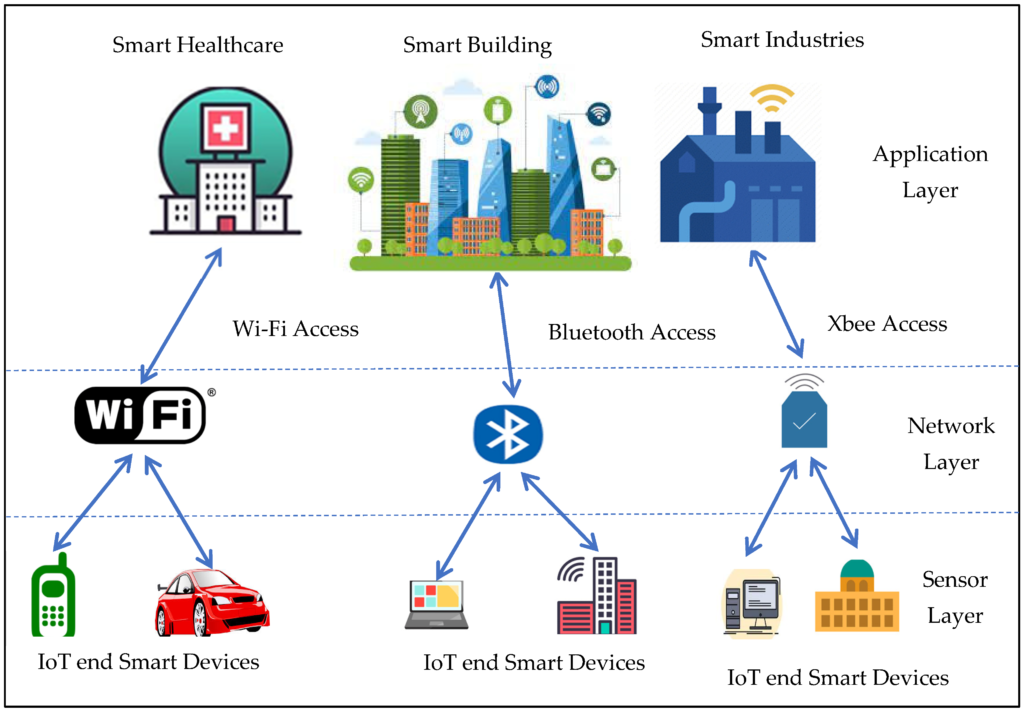
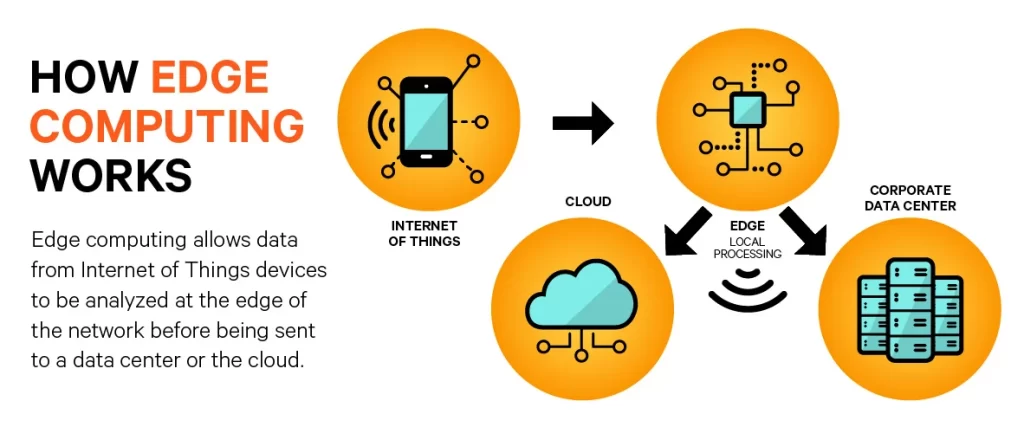
Implications for Businesses
The adoption of these emerging data technologies carries profound implications for businesses across various industries:
- Enhanced Decision-Making: AI-driven insights and predictive analytics are enabling more informed decisions. By processing vast datasets and identifying intricate correlations, businesses can tailor their strategies, optimize operations, and enhance customer experiences.
- Data Security: Blockchain technology ensures data security and privacy. It offers transparency and immutability, making it exceptionally difficult for unauthorized parties to alter records. This is especially valuable for industries where data integrity is paramount, such as finance and healthcare.
- Efficiency and Productivity: Edge computing, combined with the power of 5G, is poised to significantly boost efficiency and productivity. Data can be processed closer to its source, reducing the need for centralized data centers and enabling real-time analysis. This shift is instrumental in optimizing supply chain logistics, energy management, and more.
- Competitive Edge: Early adoption of emerging technologies can provide a substantial competitive advantage. Companies that embrace these innovations can lead the way in their respective markets, attracting tech-savvy customers and fostering innovation.
Agentic AI
What it is:
Agentic AI refers to systems that act autonomously to achieve goals on behalf of users or organizations. Unlike passive models that only respond to prompts, agentic AI can plan, take multi-step actions, evaluate outcomes, and update strategies without human micromanagement.
Why it matters:
Agentic systems can automate complex workflows, orchestrate data and services across systems, and reduce operational friction—freeing human teams to focus on strategy rather than repetitive execution.
Use cases:
- Automated customer onboarding: agent coordinates identity checks, provisioning, and communications.
- IT ops: proactive remediation of incidents by diagnosing root causes and applying fixes.
- Marketing orchestration: launching, optimizing, and reporting campaigns across channels.
Implementation tips:
- Start with clearly defined, bounded tasks (e.g., “resolve category X incidents”).
- Implement fail-safe controls, human-in-the-loop checkpoints, and audit logs.
- Focus on transparency: log decisions and reasoning to build trust and compliance.
AI That Actually Reasons Through Problems
What it is:
Reasoning AI extends beyond pattern recognition to bridge facts, causality, and multi-step logic—capable of forming hypotheses, testing them, and deriving explanations for decisions.
Why it matters:
Applications that require explanation, legal reasoning, strategic planning, or scientific inference benefit from models that can justify recommendations rather than only outputting predictions.
Use cases:
- Financial risk analysis that explains drivers of default probability.
- Clinical decision support providing reasoning for suggested treatment paths.
- Strategic scenario planning where trade-offs and assumptions are surfaced.
Implementation tips:
- Combine symbolic methods (rules, knowledge graphs) with statistical models to improve explainability.
- Use thorough evaluation frameworks: chain-of-thought testing, counterfactuals, and adversarial scenarios.
- Integrate human review for high-stakes outputs.
Multimodal AI
What it is:
Multimodal AI processes and reasons across multiple data types—text, image, audio, video, and structured data—enabling richer understanding and more natural interactions.
Why it matters:
Real-world problems rarely live in a single modality. Multimodal systems unlock new capabilities like automated video summarization, product understanding from images + descriptions, and multimodal search.
Use cases:
- Customer support that ingests screenshots, chat logs, and call transcripts to diagnose issues.
- Manufacturing: combine sensor telemetry with camera feeds and maintenance logs for root-cause analysis.
- Media: automatically tag and summarize multimedia content for faster discovery.
Implementation tips:
- Start with focused multimodal tasks (e.g., image + caption alignment) before expanding scope.
- Ensure synchronized data and timestamp alignment for multimodal fusion.
- Invest in annotation pipelines that capture multimodal labels consistently.
AI for Scientific Breakthroughs
What it is:
AI accelerates scientific discovery by automating literature review, suggesting experiments, optimizing simulations, and identifying previously hidden patterns in research data.
Why it matters:
AI shortens R&D cycles, reduces cost of experimentation, and expands the scale of hypothesis testing—fueling breakthroughs in drug discovery, materials science, climate modeling, and genomics.
Use cases:
- Drug candidate generation and in-silico screening.
- Materials discovery by predicting properties from molecular structure.
- Climate model refinement using pattern discovery in sensor networks.
Implementation tips:
- Partner domain experts with data scientists to frame meaningful hypothesis spaces.
- Use open benchmarks and reproducible pipelines to validate discoveries.
- Prioritize interpretability and reproducibility—publish models and datasets where possible.
AI in Autonomous Systems
What it is:
AI embedded in physical systems—robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, industrial agents—that perceive, plan, and act in the real world.
Why it matters:
Autonomous systems promise operational scale, continuous operation, and access to environments that are hazardous or remote—transforming logistics, agriculture, security, and manufacturing.
Use cases:
- Autonomous delivery drones or warehouse robots.
- Agricultural robots for precision weeding and harvesting.
- Industrial inspection robots for infrastructure monitoring.
Implementation tips:
- Build rigorous simulation environments to test wide failure modes before real-world deployment.
- Layer perception, planning, and control with safety constraints and redundancy.
- Maintain continuous monitoring and rollback pathways for unexpected behavior.
Strategic Implementation Guide for High-Growth Companies
Phased roadmap:
- Discovery & Prioritization: map business goals to AI opportunities; score by impact, effort, and risk.
- Pilot & Validate: small, measurable pilots with clear success metrics.
- Scale & Integrate: productionize winners, integrate into processes and systems.
- Operationalize Governance: policies for data, model lifecycle, monitoring, and compliance.
- Continuous Improvement: feedback loops from users and monitoring to refine models.
Organizational enablers:
- Executive sponsorship and cross-functional steering committee.
- Dedicated product-oriented AI teams (data engineers + ML engineers + domain PMs).
- Clear KPIs: time-to-insight, error reduction, revenue uplift, cost savings.
Risk controls:
- Model validation pipelines, bias audits, and incident playbooks.
- Access controls, data lineage, and retention policies.
Implementation Playbooks for Key Business Functions
Marketing:
- Use-case: predictive lead scoring.
- Steps: ingest CRM + engagement data → feature engineering → model training → scoring → integrate into campaign workflow → measure conversion lift.
- KPIs: MQL-to-SQL conversion, CAC reduction.
Sales:
- Use-case: deal risk prediction.
- Steps: combine CRM, usage, and contract data → build risk model → surface at-risk deals to reps → trigger interventions.
- KPIs: deal velocity, churn reduction.
Customer Support:
- Use-case: automated triage.
- Steps: train classifier on tickets + attachments → auto-route + suggest responses → human review loop.
- KPIs: resolution time, CSAT.
Supply Chain / Ops:
- Use-case: demand forecasting.
- Steps: fuse POS, seasonal, promotions data → probabilistic forecasts → inventory optimization.
- KPIs: stockouts, inventory turnover.
Finance / Risk:
- Use-case: fraud detection.
- Steps: establish streaming anomaly detection → enrichment with contextual data → scoring and case management.
- KPIs: fraud loss reduction, false-positive rate.
Implementation Resources and Partners
Internal resources to build:
- Data platform (warehouse/lake + ETL pipelines)
- MLOps stack (model registry, CI/CD, monitoring)
- Annotation / labeling infrastructure
- Governance framework and documentation portal
Types of partners to consider:
- Cloud providers (for compute, managed ML services)
- Specialist AI consultancies (for strategy and rapid pilots)
- Data-labeling vendors (for human-in-the-loop workflows)
- Industry software partners (vertical tools with integrated models)
Selection tips:
- Prioritize partners with proven domain experience.
- Prefer modular tools that integrate with existing stacks.
- Seek partners committed to knowledge transfer and measurable outcomes.
Why These Technologies Will Change Everything (And How to Get Ahead)
Why they’ll change everything:
- Scale and Speed: agentic and multimodal AIs automate complex decision chains and handle rich, real-world inputs—dramatically multiplying productivity.
- New Business Models: AI-enabled automation and prediction create products and services that were previously infeasible (e.g., personalized medicine, fully automated logistics).
- Democratization of Expertise: reasoning AI and augmented analytics push expert-level decision support into the hands of everyday users.
- Real-World Autonomy: autonomous systems expand operations into new physical domains—reducing costs and enabling 24/7 service.
- Accelerated Innovation: AI-driven scientific discovery compresses R&D timelines and unlocks breakthroughs across industries.
How to get ahead (practical checklist):
- Define Strategic Use Cases: align tech pilots with measurable business outcomes.
- Invest in a Robust Data Foundation: clean, integrated, and governed data is the non-negotiable baseline.
- Adopt a Product Mindset: treat AI features as products—iterate fast, measure, and optimize.
- Build Cross-Functional Teams: mix domain experts, data engineers, ML engineers, and product managers.
- Start Small, Scale Fast: validate with pilots, then operationalize winners with MLOps.
- Prioritize Safety & Ethics: put governance, monitoring, and human oversight front and center.
Cultivate Partnerships: leverage cloud and specialist partners to accelerate capability building.
Preparation for the Future
To harness the potential of emerging data technologies and stay ahead in this data-driven era, it’s essential to be prepared:

- Continuous Learning: Invest in ongoing education and training for your team. Staying informed about the latest developments in data technologies and gaining expertise in their application is pivotal to keeping your organization competitive.
- Evaluate Relevance: Assess the relevance of each emerging technology to your business goals and industry. Not every technology may be suitable for your organization, so focus on those that can bring tangible benefits.
- Security Measures: Vigilance about data security and privacy is crucial. New technologies often come with new security concerns. Stay informed about the potential risks and safeguards associated with each technology.
- Experiment and Pilot: Consider initiating pilot projects to test the feasibility and impact of emerging technologies within your organization. This allows you to evaluate their potential benefits and shortcomings without making extensive commitments.
The data tech revolution is underway, and it’s changing the way we work with data. By staying informed, continuously learning, and strategically implementing emerging technologies, you can position yourself and your organization for a future where data technologies play an increasingly central role in our daily lives and industries.
Conclusion
The data landscape is evolving at breathtaking speed—and the technologies shaping it are no longer incremental upgrades, but transformational catalysts. From agentic AI that can autonomously reason and act, to multimodal systems that interpret the world like humans do, to quantum and scientific AI unlocking discoveries once thought impossible—the future of data is intelligent, autonomous, and deeply integrated across every industry.
Businesses that embrace this shift early will unlock powerful competitive advantages: faster decisions, sharper predictions, lower operational cost, and entirely new value models born from automation and insight. But success demands more than adoption—it requires strategy. High-growth organizations must build strong data foundations, invest in people and experimentation, and approach implementation with discipline, governance, and measurable outcomes.
We are entering a new era where data isn’t just a resource—it is a living system driving innovation, intelligence, and opportunity. The companies and professionals who learn, experiment, and evolve with these technologies will lead the next wave of breakthroughs.
The future of data is already here. The question now is not whether to adapt, but how fast you are ready to move.
FAQ’s
What are the emerging data technologies?
Emerging data technologies include AI-driven analytics, cloud data platforms, edge computing, real-time data processing, and data fabric solutions, enabling faster, smarter, and more scalable data management and insights.
What are the top 5 technologies currently being used in data science?
The top 5 technologies in data science are Python/R programming, SQL and NoSQL databases, cloud computing platforms, machine learning frameworks, and data visualization tools, powering analysis, modeling, and insights across industries.
What are the 5 latest technologies?
Five of the latest technologies include artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, quantum computing, edge computing, and augmented/virtual reality (AR/VR), driving innovation across industries and transforming how we interact with data and devices.
What is the big five in tech?
The Big Five in tech refers to Apple, Microsoft, Google (Alphabet), Amazon, and Meta (Facebook)—the largest and most influential technology companies shaping global innovation and digital markets.
What are the top 3 trends in data science?
The top three trends in data science are AI and machine learning integration, real-time and streaming analytics, and augmented analytics with automated insights, helping organizations make faster and smarter data-driven decisions.



